Figure 4.
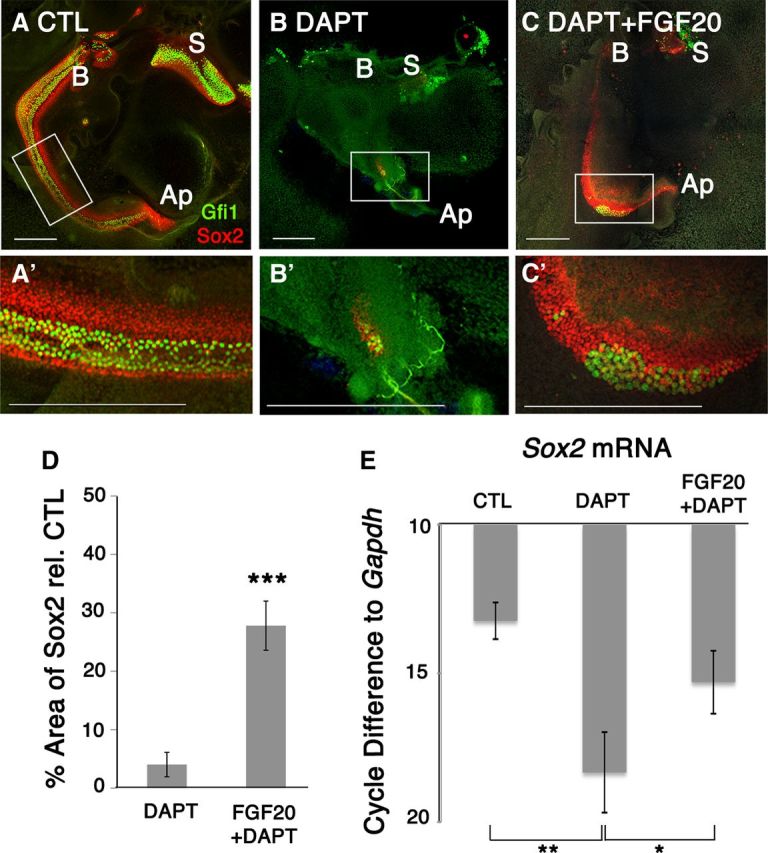
Fgf20 rescued Notch-inhibited prosensory precursors at E12.5 + 6 DIV. A, A′, Control explants show clear development of both Gfi1+ and Sox2+ sensory cells. B, DAPT treatment of E12.5 explants for 6 DIV affects sensory epithelium development. B′, Both Gfi1+ and Sox2+ cells were affected. C, Fgf20 in the presence of DAPT rescued Sox2+ cells. C′, Sox2 was predominantly rescued while Gfi1 rescue was variable. S, Saccule; B, base; Ap, apex; CTL, control. Scale bars, 200 μm. D, Quantification of Sox2+ area relative to control showed that only 4% of the sensory epithelium remained while 24% of the sensory epithelium was preserved. Students t test; ***p < 0.00005, n = 8 cochlea per condition. E, RT-qPCR analysis on E12.5 + 3 DIV explants confirms that DAPT treatment decreased Sox2 mRNA expression, while Fgf20 in the presence of DAPT rescued Sox2. Cycle differences to Gapdh with a cutoff at cycle 38. One-way ANOVA for correlated samples show statistical significance; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, n = 3 experiments.
