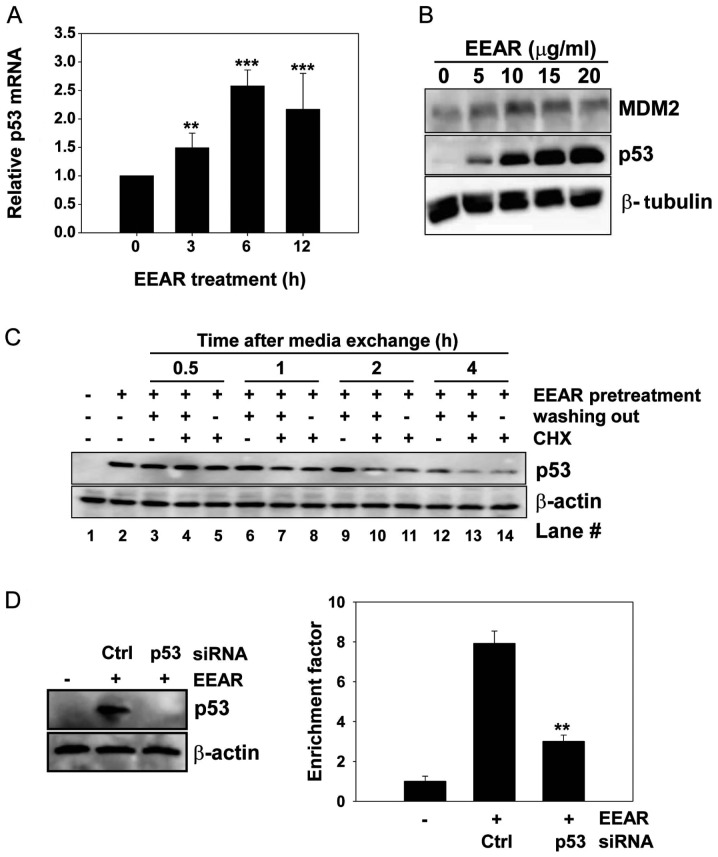
Figure 3.
p53-dependent EEAR-induced apoptosis. (A) HCT-116 cells were treated with 10 μg/ml EEAR and total RNA was isolated at the indicated time points. cDNA was synthesized using an equal amount of total RNA and subjected to RT-PCR analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate experiments. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 vs. vehicle treatment group. (B) HCT-116 cells were exposed to the indicated concentrations of EEAR for 12 h and then MDM2 and p53 proteins were detected by western blot analysis. (C) HCT-116 cells were pretreated with 10 μg/ml EEAR for 12 h then cycloheximide (CHX) was added to fresh culture medium in the absence or the presence of EEAR. Total protein was prepared with RIPA buffer at the indicated time points and subjected to western blot analysis. (D) Cells were transiently transfected with p53 or GFP control siRNA for 24 h then treated with 10 μg/ml EEAR for another 24 h. The expression of p53 was examined by western blot analysis (left) and apoptosis was quantified using ELISA as described in Materials and methods (right). Data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate experiments. **P<0.01 vs. control siRNA treatment group in the presence of EEAR exposure. EEAR, ethanol extract of A. radix; RT-PCR, real-time polymerase chain reaction; SD, standard deviation; GFP, green fluorescent protein; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.