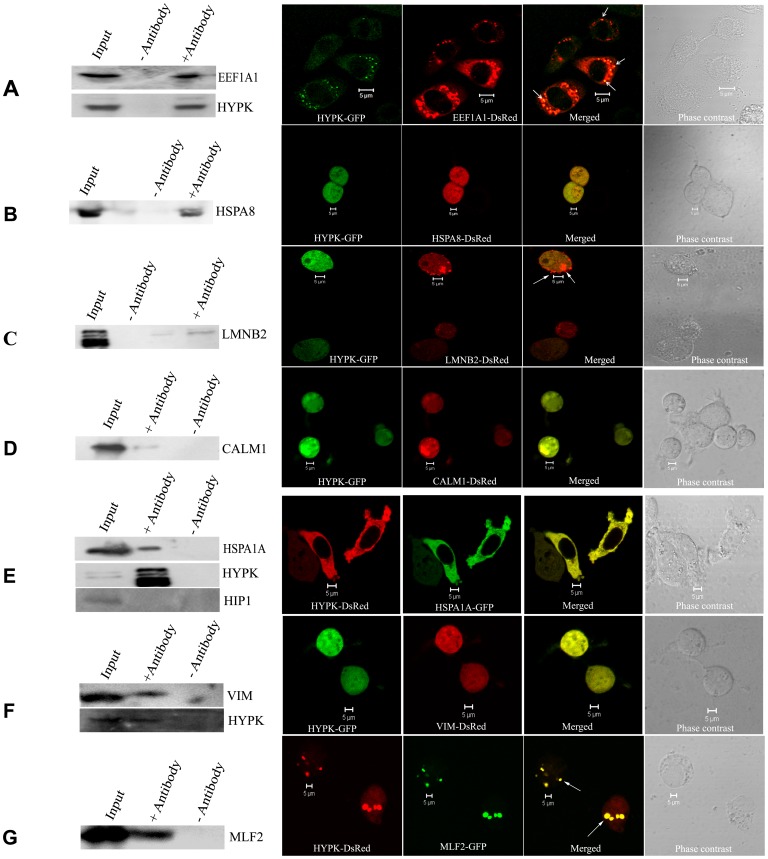
Figure 2. Validation of interaction by co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) and confocal microscopy.
Validation of interaction between HYPK and EEF1A1 by co-IP using anti-HYPK antibody (endogenous EEF1A1 was detected) along with subcellular co-localization of HYPK-GFP with EEF1A1-DsRed (A). The interaction of HYPK with HSPA8, LMNB2, CALM1, HSPA1A, VIM and MLF2 are shown (B, C, D, E, F and G respectively). The co-IP of Neuro2A SCL with anti-HYPK antibody precipitated endogenous HSPA1A (immunoblot probed with anti-HSPA1A; E). Anti-HYPK antibody was used to immunoprecipitate the HYPK-complex from Neuro2A SCL overexpressing HSPA8-DsRed (B), LMNB2-DsRed (C), CALM1-DsRed (D) or VIM-DsRed (F) and the immunoblots were probed with anti-DsRed antibody. Interaction between HYPK and MLF2 was confirmed by probing the HYPK-immunoprecipitated complex with anti-GFP antibody (G). The co-IP blots shown in A, E and F were re-probed with anti-HYPK antibody confirming HYPK in the immunoprecipitate. The dots showing co-localization of HYPK with EEF1A1 (A), LMNB2 (C) and MLF2 (G) are indicated by arrows. The immunoblot showing interaction between endogenous HYPK and endogenous HSPA1A was stripped and re-probed with anti-HIP1 antibody. The absence of HIP1 in the immunoprecipitate confirmed that HYPK did not interact with HIP1 (E). Scale bars (5 µm) for the confocal images are indicated in each panel.