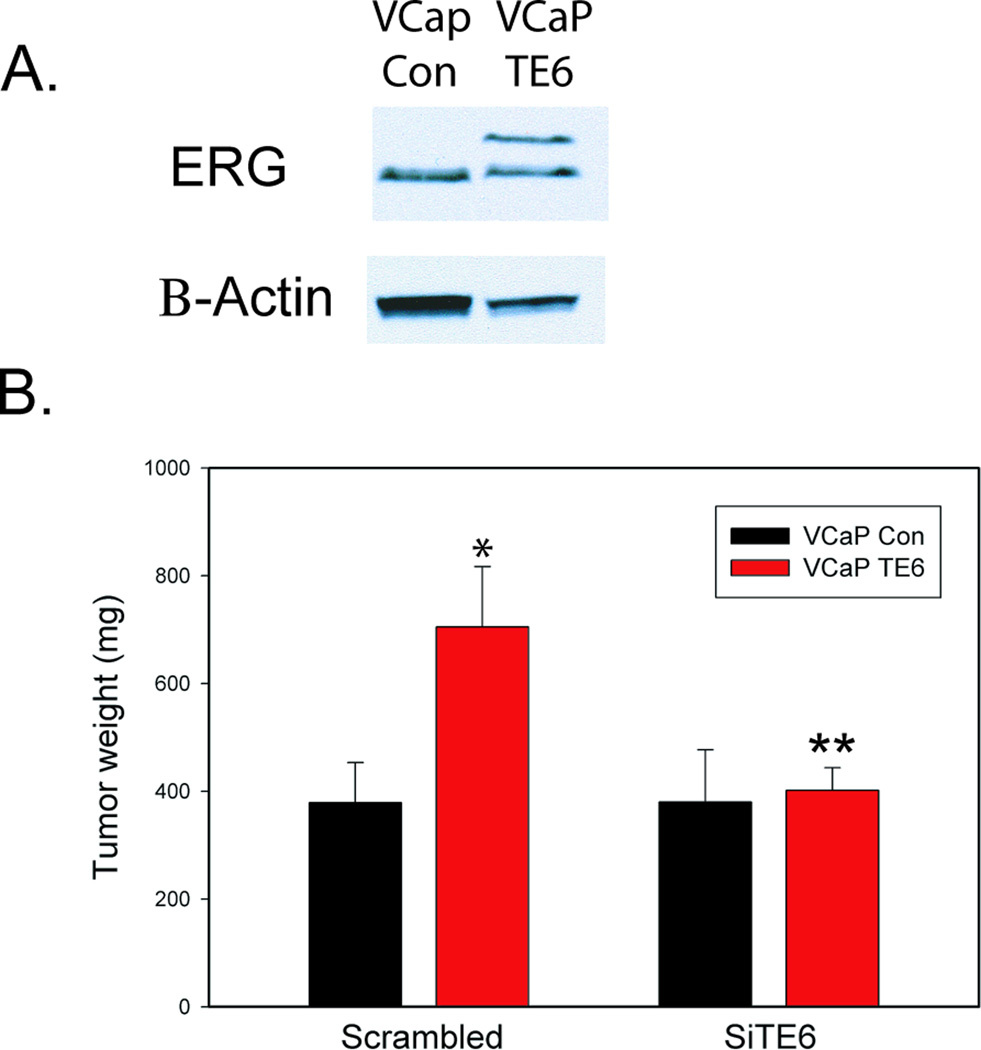
Figure 6. SiRNA targeting the Type VI T/E fusion mRNA inhibits tumor progression in vivo.
A. Expression of the Type VI fusion protein in VCAP TE 6 cells engineered to express this protein detected with anti-ERG antibody. The Type VI fusion gene isoform protein is slightly larger than the Type III fusion gene protein, which is translated beginning at methionine 40, while the Type VI protein is translated from the in-frame TMPRSS2 translation initiation codon. β-actin is a loading control. B. Subcutaneous xenografts of VCaP vector controls or VCaP expressing the Type VI fusion gene were treated with nanoliposomes containing scrambled siRNA or siRNA targeting the TE Type VI fusion junction. Final tumor weight in mg +/− SEM is shown. Six mice were used in the scrambled control groups and 8 in the SiTE6 groups. The single asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference between different cell types treated with control siRNA; double asterisks indicate a significant difference from same cell type treated with scrambled control siRNA versus targeted siRNA.