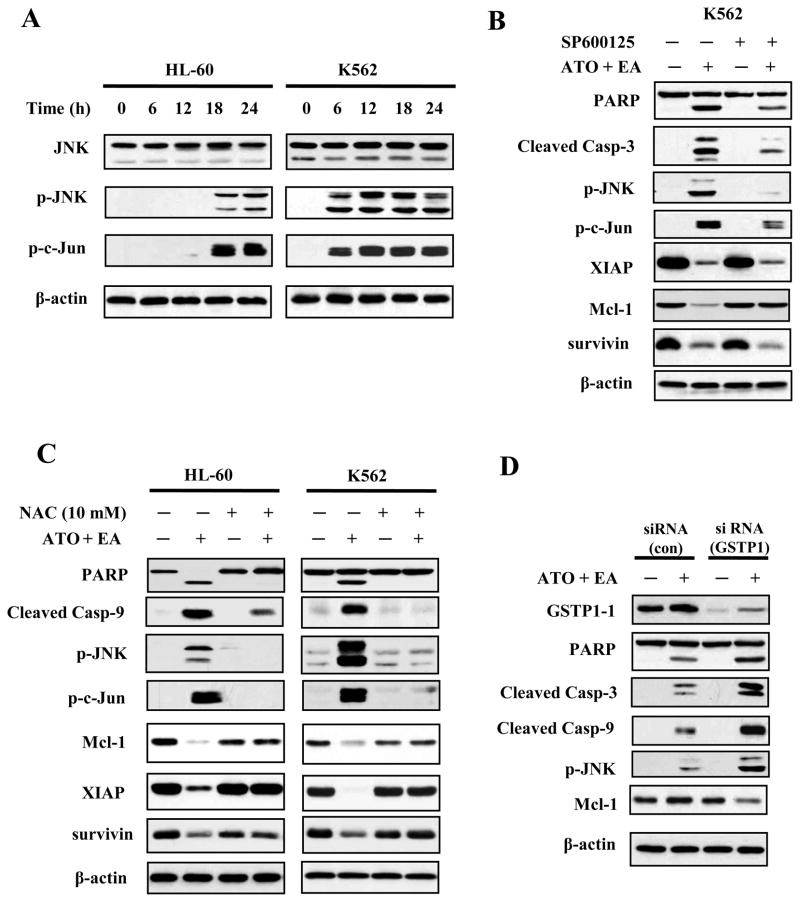
Figure 4. JNK signaling is activated by ATO/EA treatment.
(A) Activation of JNK. HL-60 and K562 cells treated with ATO/EA combinations for the indicated times, were lysed and tested for levels of total JNK protein, p-JNK and p-c-Jun, a target of JNK, using specific antibodies in a Western blot analysis. β-actin was used as a loading control. The combinations of ATO/EA are: 2μM ATO and 40 μM EA for HL-60 cells, and 2 μM ATO and 80 μl EA for K562 cells. (B) JNK activation is crucial for ATO/EA induced apoptotic pathway. K562 cells pretreated with 40 μM JNK inhibitor (SP600125) followed by treatment with ATO/EA for 24 h were used to determine the levels of PARP, caspase-3, p-JNK, p-c-Jun, XIAP, Mcl-1, survivin, and β-actin using Western blotting. (C) Treatment with an anti-oxidant NAC inhibits the apoptotic pathway. HL-60 and K562 cells were pretreated with 10 mM NAC for 4 h, followed by ATO/EA treatment for 24 h. The levels of PARP, caspase-3, -9, p-JNK, p-c-Jun, XIAP, Mcl-1, surviving and β-actin were determined using Western blotting. (D) Knock-down of GSTP1-1 enhances the activation of caspases and JNK. K562 cells were transfected with GSTP1siRNA or control siRNA and after 18 h treated with 2 μM ATO/60 μM EA for additional 24 h. Protein levels of GSTP1-1, PARP, caspase-3, -9, p-JNK, Mcl-1 and β-actin were determined with Western blotting using specific antibodies.