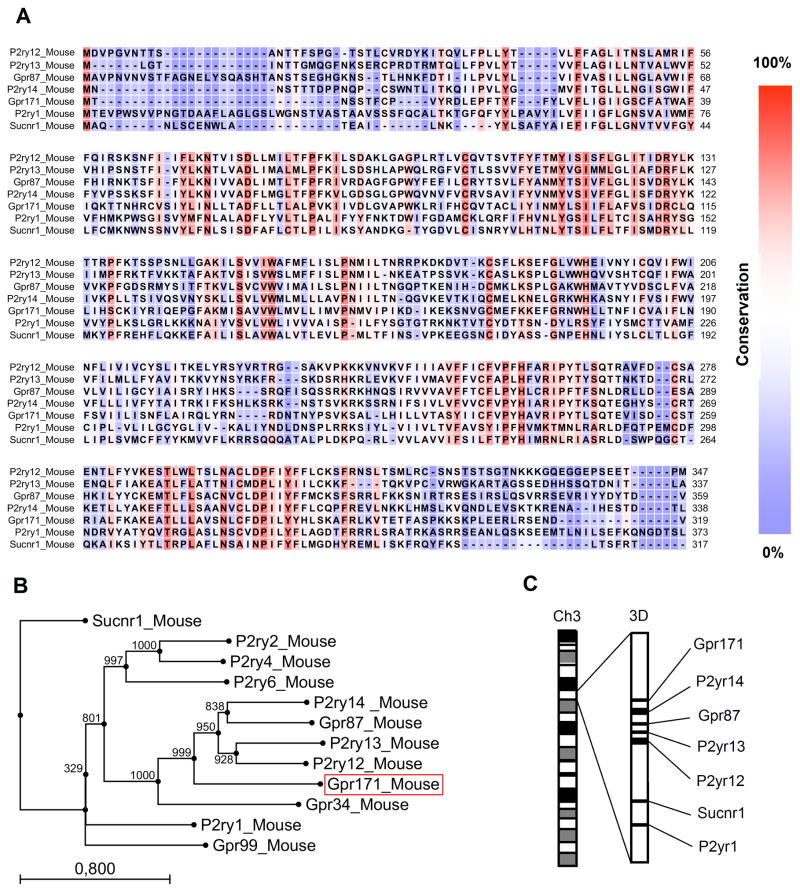
FIG. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of Gpr171. (A) Alignment of amino acid sequences of murine Gpr171 with other murine P2Y genes localized on chromosome 3. The seven transmembrane domains (indicated as TM) are overlined. As emphasized by the color scheme, the sequences display the highest degree of conservation in their TM3, TM6, and TM7 domains. (B) Phylogenetic tree illustrating how the murine orphan receptor Gpr171 is related to other members of the P2YR family. Alignment of amino acid sequences and tree reconstruction were performed using CLC Main Workbench 5. Trees were created using the Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method and 1,000 bootstraps replications were conducted. The length of each branch is proportional to evolutionary divergence. (C) Schematic representation of the reciprocal localization of Gpr171, Gpr87, P2ry12, P2ry13, P2y14, Sucnr1, and P2ry1 on chromosome 3. Co-localization of genes in the same chromosomal region strongly indicates that they evolved by gene duplication from the same ancestor gene.