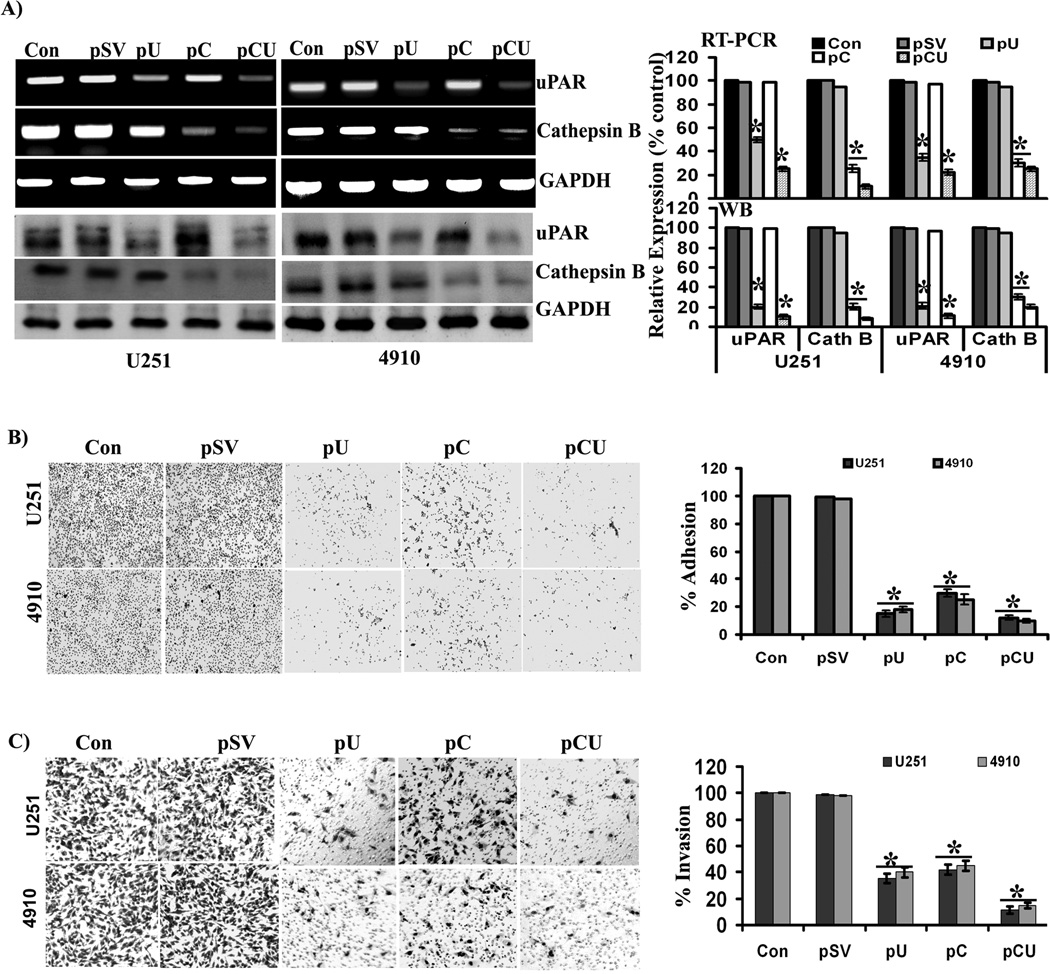
Figure 2. Efficiency of siRNA plasmid constructs and their effects on adhesion and invasion of glioma cells.
(A) Expression of cathepsin B and uPAR at the mRNA and protein levels, after transfection with pSV, pU, pC, or pCU. To determine the efficiency of siRNA plasmid constructs, U251 and 4910 cells plated on laminin-coated plates were treated with pSV, pU, pC, or pCU for 72 hrs. mRNA and protein expression levels of cathepsin B and uPAR were determined by RT-PCR and Western blot analyses, respectively. GAPDH served as a loading control. Blots are representative of three independent experiments. Mean ±SEM. *p<0.001 vs. control. (B) Adhesion assay was performed to evaluate the effects of pSV, pU, pC, and pCU on the adhesive potential of U251 and 4910 cells to laminin-coated plates. Percent of adhesion was calculated from the mean obtained from three independent experiments and are represented (±SEM). *p<0.001 vs. control. (C) Transwell invasion assay was performed to evaluate the effects of pS, pU, pC, and pCU on invasion of U251 and 4910 cells through laminin-5. Percent of invasion was calculated from the mean obtained from three independent experiments and are represented (±SEM). *p<0.001 vs. control.