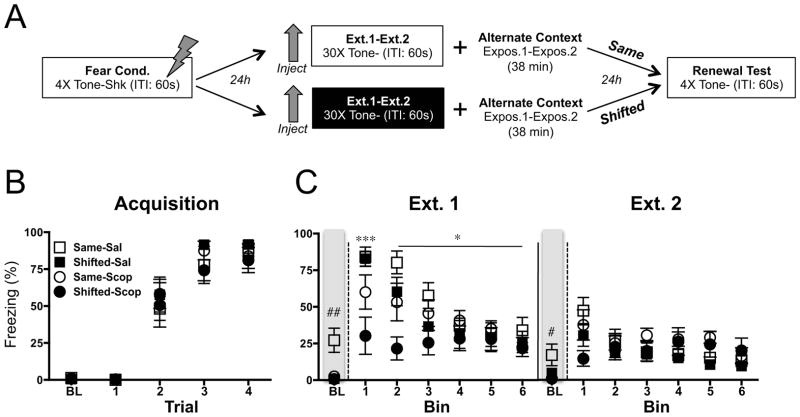
Figure 1.
Effects of scopolamine on fear extinction (two sessions). (A) Experimental design. Tone: 80 dB, 30 sec. Shock: .9 mA, 2 sec. Inter-trial Interval (ITI): 60 sec. (B) Fear acquisition. Mean (±sem) percent baseline (BL) freezing and tone freezing during each tone-footshock trial. (C) Extinction. Mean (±sem) percent freezing during baseline and each bin of 5 tone-alone presentations for extinction (ext.) sessions 1–2. Rats were extinguished in the same context as acquisition/test (Same) or in a novel context (Shifted), under scopolamine (Scop) or the vehicle saline (Sal) (n=8). Freezing during the first and second bins in the novel context was reduced by scopolamine compared to saline (***p <.001; *p <.05). Pre-extinction baseline fear was reduced for scopolamine-treated animals ((##p <.01; #p <.05).