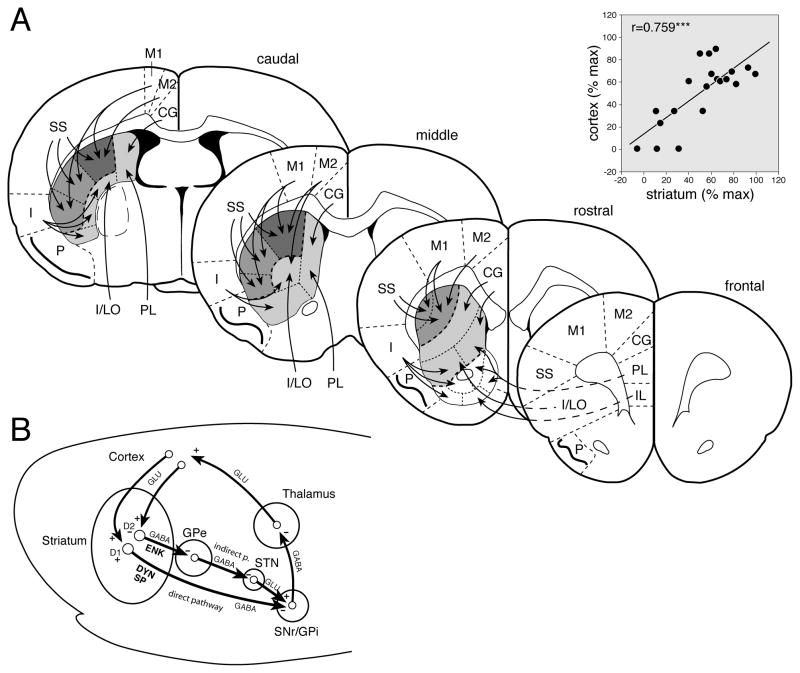
Figure 1.
Schematic illustrations of cortico-basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuits. (A) Striatal sectors used for mapping gene expression and their main cortical inputs (arrows) are shown for frontal, rostral, middle, and caudal levels of the rat forebrain (for details, see Willuhn et al., 2003; Yano and Steiner, 2005a,b). Psychostimulant-induced gene regulation is maximal in the dorsal sensorimotor sectors of the middle and caudal striatum (darkest shading), which receive inputs from the medial agranular (M2), primary motor (M1), and somatosensory (SS) cortex (see Section 3.1.2). Limbic (white), associative (light grey), and sensorimotor sectors (darker grey) are indicated. The scatterplot (inset upper right) displays the association between methylphenidate-induced Zif268 expression in individual striatal sectors and Zif268 expression in their indicated cortical input regions (values averaged if more than one input). Values are differences in gene expression between animals sacrificed 40 minutes after methylphenidate administration (5 mg/kg, i.p.) and controls sacrificed immediately after drug injection, and are expressed as the percentage of maximal increase in the striatum (see Yano and Steiner, 2005a). CG, cingulate; I, insular; IL, infralimbic; I/LO, insular/lateral orbital; P, piriform; PL, prelimbic. *** p < 0.001. (B) Direct and indirect striatal output pathways in the cortico-basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuits. Direct pathway (striatonigral) neurons contain mainly D1 dopamine receptors and the neuropeptides substance P (SP) and dynorphin (DYN), whereas neurons that give rise to the indirect pathway (striatopallidal neurons) express mostly D2 receptors and the peptide enkephalin (ENK), in addition to their main neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). + and − denote facilitatory and inhibitory, respectively. GLU, glutamate; GPe, globus pallidus external segment; GPi, globus pallidus internal segment; SNr, substantia nigra pars reticulata; STN, subthalamic nucleus