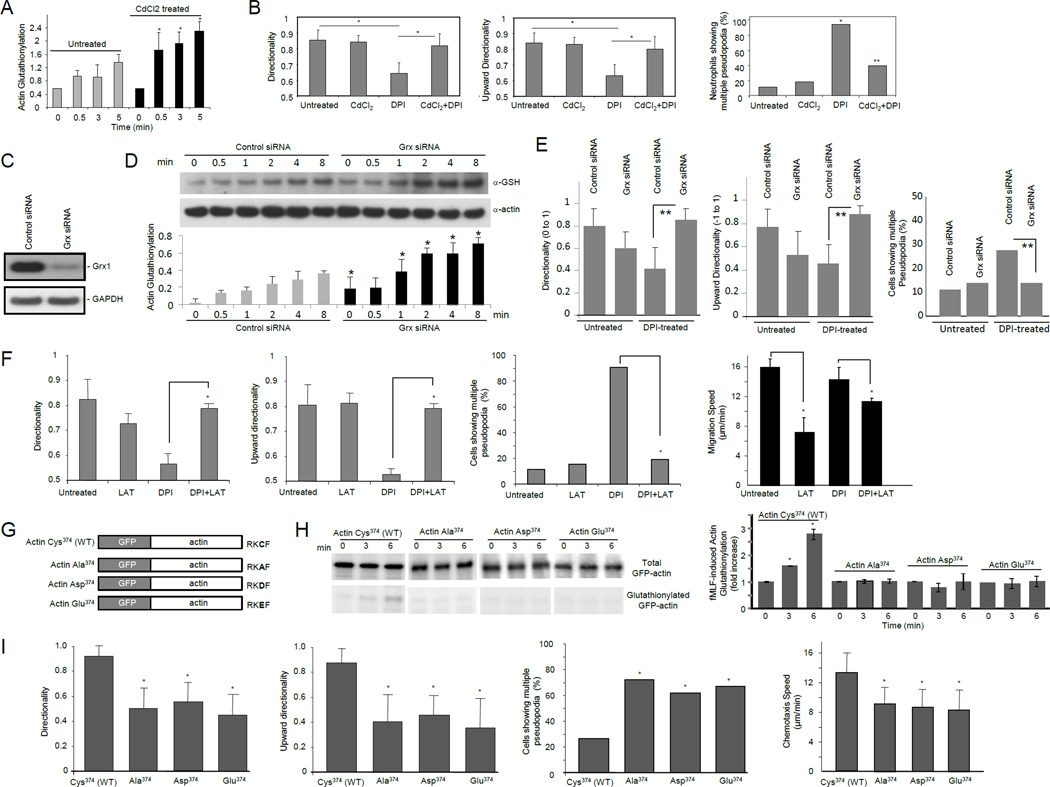
Figure 5. Neutrophil chemotaxis defects induced by ROS depletion could be rescued by inhibiting glutaredoxin.
(A) Actin glutathionylation was augmented in cells treated with CdCl2. Data represents means ± SD of three experiments. *, p<0.01 versus untreated dHL60 cells. (B) Augmenting protein glutathionylation by CdCl2 rescued DPI-induced chemotaxis defect. Neutrophils chemotaxis was analyzed as described in Figure 4E. *, p<0.05 versus untreated neutrophils; *, p<0.05 versus DPI treated neutrophils. (C) siRNA silencing of Grx1 in differentiated HL60 cells. (D) Actin glutathionylation was enhanced in cells transfected with glutaredoxin siRNA. Data represents means ± SD of three experiments. *, p<0.01 versus dHL60 cells transfected with control siRNA. (E) siRNA silencing of glutaredoxin rescued DPI-induced chemotaxis defect. **, p<0.005 versus dHL60 cells transfected with control siRNA. (F) ROS depletion-induced formation of multiple pseudopodia and impaired directional migration were partially rescued by treatment with latrauculin B. Mouse neutrophils were pretreated with 50 µM DPI, 5 nM latrauculin B (LAT), 5 nM LAT + 2 µM CdCl2, or left untreated, and then exposed to a chemoattractant gradient generated by addition of 100 nM fMLF (1 µl) in the EZ-taxiscan device. *, p<0.005. (G) Schematic representation of wild-type and mutant forms of human β-actin fused with GFP. (H) Cys374 is critical for ROS-elicited actin glutathionylation. dHL60 cells overexpressing indicated protein were stimulated with 1µM fMLF. Overexpression of wild-type and mutant forms of GFP-actin was confirmed by western blotting with a GFP antibody. Ratio of glutathionylated GFP-actin to total GFP-actin was calculated as actin-glutathionylation. Shown in the bar-graph are the fold increases of actin-glutathionylation compared to unstimulated cells (time 0). Data represents means ± SD of three experiments. *, p<0.01 versus unstimulated cells. (I) Glutathionylation at actin-Cys374 is a key regulatory mechanism for efficient neutrophil chemotactic migration. Cells overexpressing EGFP-actin were identified by their higher fluorescent intensity compared with untransfected cells. The chemotaxis of transfected dHL60 cells was analyzed using an EZ-taxiscan device as described above (n>20 cells; *, p<0.005 versus dHL60 cells expressing wild-type actin).