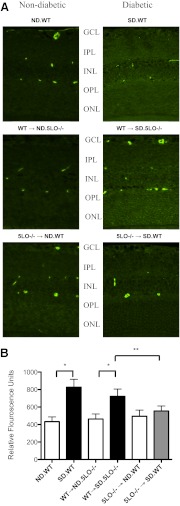
Figure 5. Inhibition of retinal vascular permeability as measured by albumin extravasation.
Retinal sections were stained for albumin as mentioned in Materials and Methods, and the intensity of fluorescence for a 0.1-mm2 area of retina was measured using Eclipse 80i and NIS-Elements AR 3.0 software. (A) A representative immunofluorescent-stained retinal slice is shown from each group of mice. Diabetic mice with circulating WT leukocytes exhibited increased microvascular vascular leakage compared with the matched ND control mice, as indicated by intense staining for albumin throughout the retinal layers, whereas the ND and diabetic mice with circulating 5LO−/− leukocytes showed diminished microvascular leakage, as indicated by very faint staining for albumin. Punctate, intense staining corresponds with cross-sections of vessels with remaining intravascular albumin. (B) The average fluorescence for each group by selection of nonvessel-containing areas of each retinal layer is summarized in the accompanying graph. Data represent three to four mice/group. *, **P<0.05.