Figure 5.
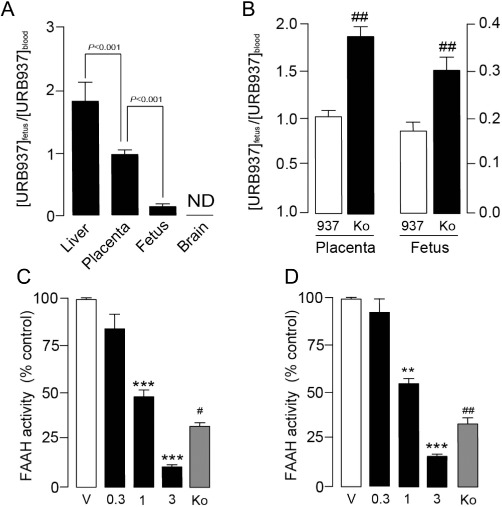
Abcg2 controls the access of URB937 to the fetus and placenta in pregnant rats. (A) Tissue:blood ratios of URB937 (1 mg·kg−1, o.g.) in various tissues of gestating (E15) female rats (ND, not detected). (B) Effect of pretreatment with the Abcg2 inhibitor Ko-143 (Ko, 10 mg·kg−1, s.c.) on the tissue:blood ratio of URB937 (937, 1 mg·kg−1, o.g.) in rat placenta and fetus. FAAH activity in (C) placenta and (D) fetus of pregnant (E15) rats 1 h after administration of vehicle (V), URB937 (0.3–3 mg·kg−1, s.c.). Abcg2 contribution to fetoprotection was assessed by injecting Ko-143 (Ko, 10 mg·kg−1, s.c) 20 min before URB937 (1 mg·kg−1, o.g.) administration. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM; n= 6–12. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 versus vehicle; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 versus URB937 (1 mg·kg−1, o.g.).
