Table 1.
Cuprate addition/phosphate acid cleavage sequence.
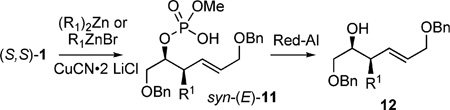 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | (R1)2Zn or R1ZnBr |
Phosphate acid - 11 yield (dr) |
Homoallylic alcohol - 12 |
% Yield |
| 1 | Me2Zn[a] | 99% (20:1) 11a |
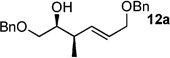 |
83 |
| 2 | Et2Zn[a] | 99%(>20:1) 11b |
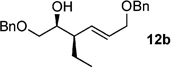 |
90 |
| 3 | iPr2Zn[a] | 99%(>20:1) 11c |
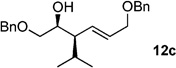 |
95 |
| 4 | cHexZnl[b] | 99% (>20:1) 11d |
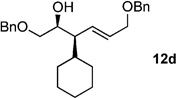 |
70 |
| 5 | BnZnBr[b] | 99% (>20:1) 11e |
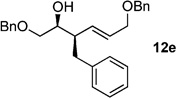 |
84 |
| 6 | CN(CH2)3ZnBr[b] | 99% (>20:1) 11f |
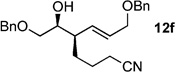 |
31 |
| 7 | Cl(CH2)4ZnBr[b] | 99% (>20:1) 11g |
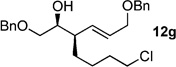 |
71 |
| 8 | CH2=CH(CH2)3ZnBr[b] | 99% (>20:1) 11h |
 |
65 |
Method required 4–5 equiv. of organocuprate.
Method required 8–9 equiv. of organocuprate.
