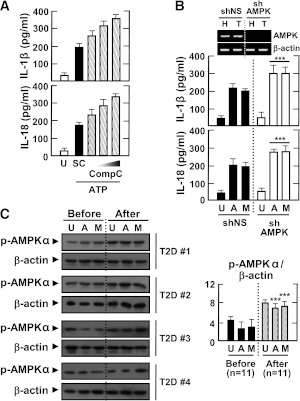
FIG. 6.
AMPK pathway activation inhibits the induction of IL-1β and IL-18 production by various inflammasome stimuli in LPS-primed MDMs. Primary MDMs were isolated from healthy controls (A and B; n = 5) or type 2 diabetic patients (C; n = 11) before and after treatment with metformin for 2 months. A: MDMs were primed with LPS (10 ng/mL) for 4 h in the presence of a high glucose concentration (15 mmol/L) and then treated with compound C (Comp C; 5, 10, or 25 μmol/L) and stimulated with ATP (1 mmol/L for 1 h). Data are expressed as means ± SEM of five independent experiments. B: MDMs were transduced with nonspecific control shRNA lentiviral particles (shNS) or lentiviral shRNA specific for AMPK (shAMPK). Then, the cells were primed with LPS (10 ng/mL) for 4 h in the presence of a high glucose concentration (15 mmol/L) and treated with ATP or MSU (100 μg/mL for 6 h). Data are expressed as means ± SEM of three independent experiments. Representative images of semiquantitative RT-PCR gels run to assess transduction efficiency (top). C: The cells were primed with LPS (10 ng/mL) for 4 h in the presence of autologous sera and then treated with ATP or MSU. A and B: ELISA of IL-1β and IL-18 levels. C: Western blotting analysis of p-AMPKα protein levels. The intensity of each band for each protein was quantified and normalized to the housekeeping protein β-actin (C, right). Data are expressed as means ± SEM. ***P < 0.001 vs. control cultures. U, untreated; SC, solvent control; A, ATP; M, MSU; Before, before treatment with metformin; After, after treatment with metformin.