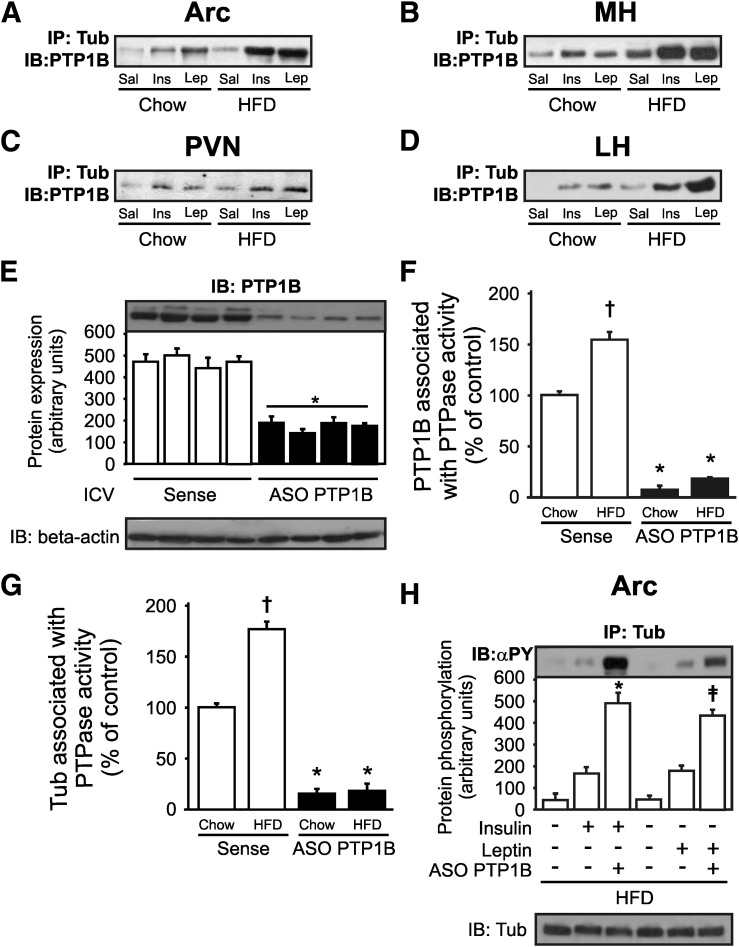
FIG. 7.
Tub/PTP1B association in response to insulin or leptin is higher in hypothalamic nuclei of mice fed a HFD. A–D: Representative blots show Tub/PTP1B association in response to ICV insulin (2 µg) or leptin (10 ng) in mice fed chow. This effect is greater in mice fed a HFD in Arc, MH, PVN, and LH of mice fed chow and HFD. E: PTP1B expression is reduced in mice fed a HFD treated with PTP1B ASO for 5 days. F: PTPase activity is increased by HFD and is reduced by PTP1B ASO treatment in mice fed a HFD. G: Tub associated with PTPase activity is greater in mice fed a HFD and is decreased by PTP1B ASO treatment. In this experiment, hypothalami were homogenized and centrifuged, and the supernatants were immunoprecipitated with anti-Tub antibody. Then, immune complexes were incubated with pp60c-src COOH-terminal phosphoregulatory peptide (TSTEPQpYQPGENL; Biomol) for 1 h at 30°C. To determine PTPase activity in a spectrophotometer, 40-μL aliquots with 100 μL Biomol Green reagent (Biomol) were used. H: Tub tyrosine phosphorylation in response to insulin or leptin is higher in mice fed a HFD treated with PTP1B ASO than in sense-treated mice. Data are presented as means ± SD from five mice per nucleus. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest was used. *P < 0.05 vs. sense, †P < 0.05 vs. mice fed chow treated with sense, ‡P < 0.05 PTP1B ASO groups. PTP1B, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; Sense, ASO control.