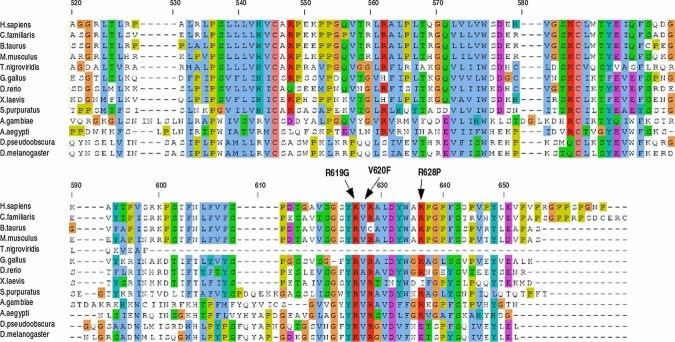
Fig 1.
Multiple alignment of proteins homologous to residues 523–653 of the human IDUA protein. The C-terminus of the human IDUA, which does not have a counterpart in many of the proteins from the glycohydrolase family 39, is conserved among multiple species. The residues affected by mutations in MPS I are shown by the arrows. The numbering of residues corresponds to human IDUA. Accession numbers of the sequences used in the alignment: Homo sapiens: NP_000194.2, Canis familiaris: Q01634, Bos taurus: XP_877410.2, Mus musculus: NP_032351.1, Tetraodon nigroviridis: CAG12584.1, Gallus gallus: NP_001026604.1, Danio rerio: CAM46905.1, Xenopus laevis: AAH77919.1, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus: XP_796813.2, Anopheles gambiae: XP_314521.3, Aedes aegypti: EAT44203.1, Drosophila pseudoobscura: XP_001356788.1, Drosophila melanogaster: NP_609489.1. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at http://www.interscience.wiley.com.]