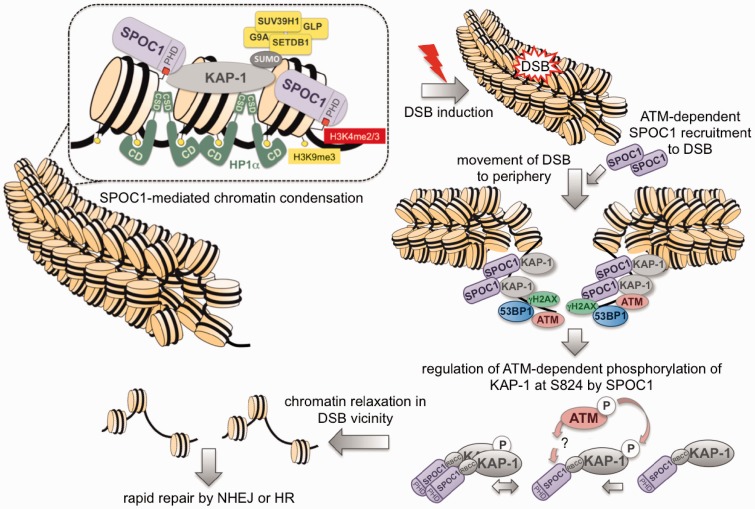
Figure 8.
Model: mechanisms of SPOC1-associated chromatin compaction and modulation of DDR at DSBs. The interaction of SPOC1 with heterochromatin building factors KAP-1, HP1 and H3K9 KMTs and its binding to chromatin via H3K4me2/3 and/or other factors can induce chromatin compaction. DNA damage-induced DSBs in heterochromatin activate ATM kinase. This results in pan-nuclear KAP-1S824 phosphorylation and concomitant ATM recruitment to repair foci, and also to increasing accumulation at repair foci. SPOC1 is also ATM-dependently recruited to DSBs and accumulates detectably only at heterochromatic repair foci after γ-H2AX expansion and 53BP1 accumulation. The KAP-1S824 phosphorylation required for chromatin relaxation at DSBs in heterochromatin and for DNA repair is regulated by SPOC1. For more details see text.