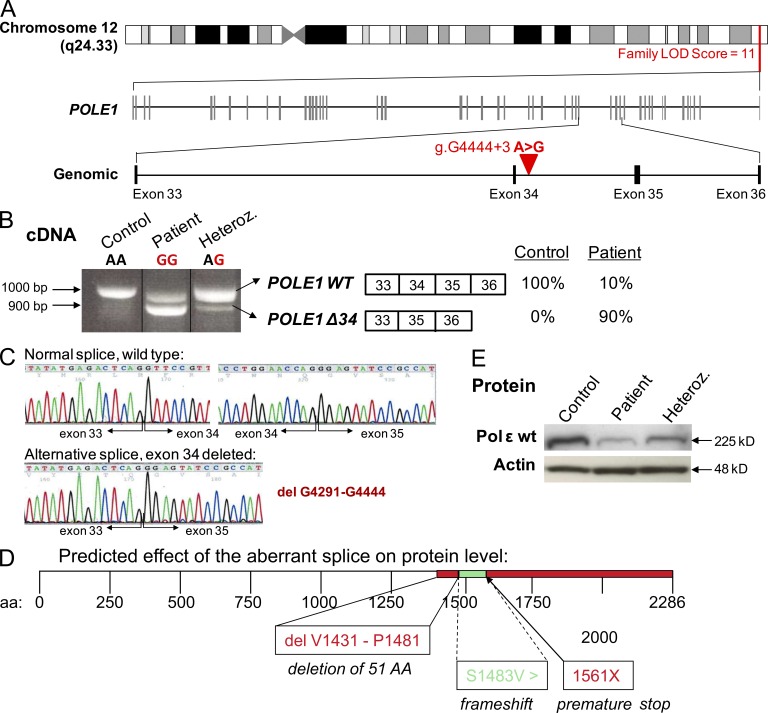
Figure 2.
Homozygous single base pair substitution in POLE1. (A) Schematic representation of the candidate interval on the long arm of chromosome 12 defined by linkage analysis and the intronic nucleotide substitution (g.G4444+3 A>G) between exons 34 and 35. (B) At the cDNA level, the mutation results in two distinct POLE1 transcripts, a WT transcript (POLE1 WT) and a transcript deleted of exon 34 (POLE1 Δ34), accounting for 10% and 90% of the POLE1 transcript expressed in patients cells, respectively. (C) Electropherograms of POLE1 cDNA obtained by sequencing the upper and lower bands, highlighting the exon 34 deletion in the lower band (bottom left). (D) Schematic representation of the predicted effect of the aberrant splice on the Pole1 protein. The intronic mutation results in an alternative splice, which deletes 51 aa in the WT protein leading to frameshift and premature stop codon at position 1561. (E) Polε1 protein levels in LBLs from a FILS patient (VI-29) and a heterozygous individual (V-9) compared with a control subject. Actin was used as a loading control. This Western blot is representative of three experiments.