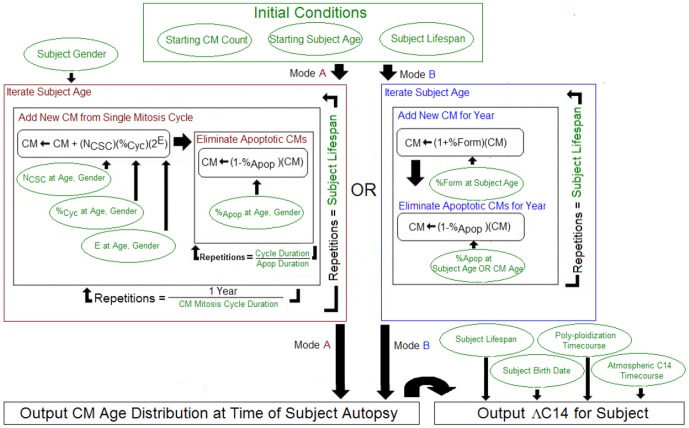
Figure 1. Hybrid Model Automaton Algorithm.
Subject hearts are modeled by initiating a “Starting CM Count” for the subject at the “Start Age” of the simulation (typically birth) and a “Subject Lifespan” that determines the number of year-repetitions. An age distribution of CM at the time of subject autopsy is produced either via Mode A or Mode B. Mode A uses variables and formulas from the Kajstura methodology to perform iterations of CM creation and destruction throughout each year-iteration according to the duration and frequency of these cycles. In this formulation, NCSC = Number of Cardiac Stem Cells, %Cyc = Fraction of CSCs cycling, and E = Number of CSC divisions occurring before loss of pluripotency. Alternatively, Mode B uses input annual creation and destruction values directly and these values may be dependent on either the patient age (at time of CM formation or at current iteration of production/destruction) or on the age of the CM undergoing destruction. There are two main outputs: (1) a distribution of surviving CM by CM age and (2) an end average C14 measurement, modeling the Bergmann methodology applied to model hearts, which is produced by incorporation of the CM age distribution with atmospheric C14 timecourse data and human polyploidization magnitudes/rates.