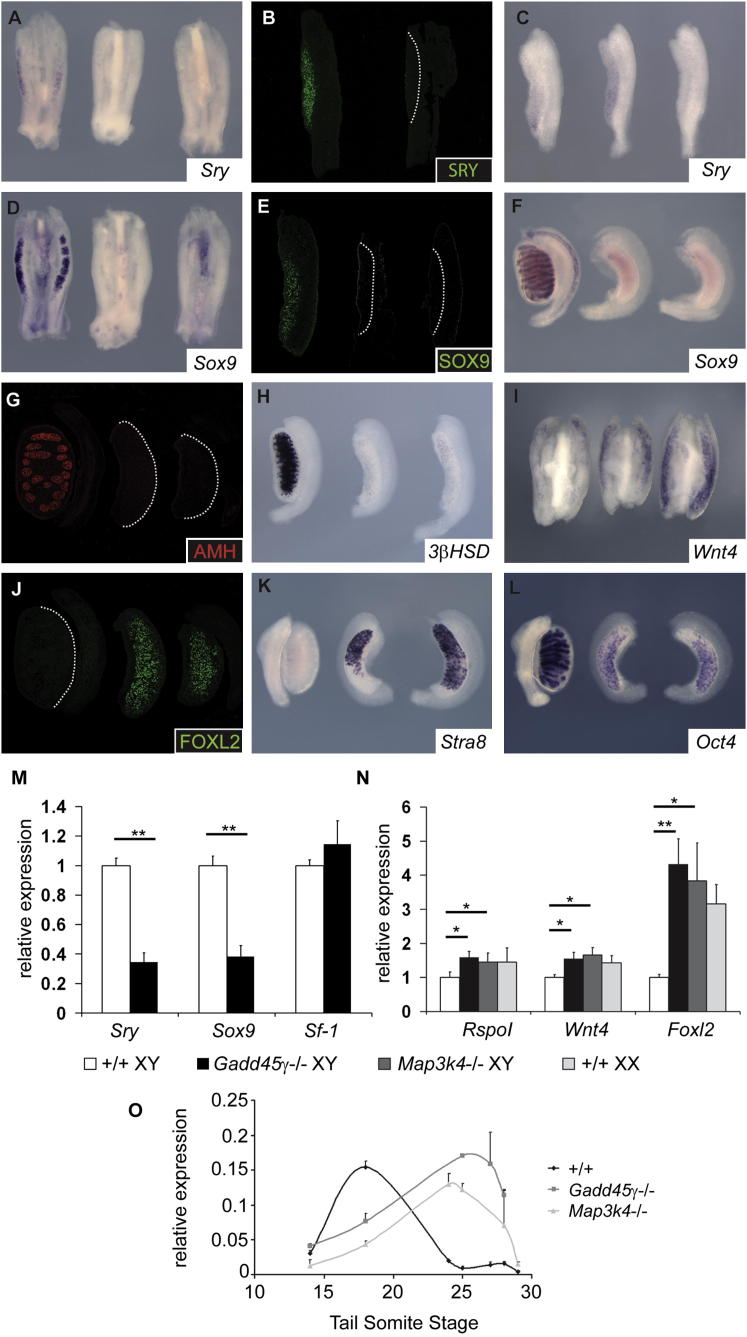
Figure 3.
XY Gonadal Sex Reversal in Gadd45γ-Deficient Embryos Is Caused by Disrupted Sry Expression
(A–L) Frames containing three gonadal tissue samples have the order, from left to right, XY wild-type, XY Gadd45γ−/−, and XX wild-type. WMISH reveals reduction in Sry transcripts detected at 11.25 dpc (16 ts) in XY mutants (A). SRY protein levels are similarly diminished in mutants (B, mutant on right). By 12.5 dpc, Sry expression is detectable at higher levels in the mutant XY gonad, in contrast to negligible levels in the XY wild-type (toward posterior of gonad) and XX control at the same stage (C). Sox9 transcripts are undetectable in mutant gonads at 18 ts (D) and 14.5 dpc (F), and SOX9 protein is also not detected at 11.5 dpc (E). AMH is also undetectable in mutant XY gonads at 14.5 dpc (G), and 3βHSD is absent at 13.5 dpc (H). Wnt4 is expressed in mutant XY gonads at 11.5 dpc (I). FOXL2 and Stra8 are expressed at high levels in mutant XY gonads at 14.5 dpc (J and K, respectively), concomitant with downregulation of Oct4 expression (L).
(M–O) Loss of Sry and Sox9 expression in XY mutant gonads was confirmed by qRT-PCR (M) at 18 ts, as was inappropriate expression of ovarian marker genes (N). qRT-PCR reveals a delay in Sry expression in Gadd45γ−/− and Map3k4−/− gonads (O). Error bars, SEM. Dotted white lines mark the boundary between gonad and mesonephros in samples that do not exhibit significant expression of marker protein.
See also Figure S1 and Figure S2 for additional phenotypic analyses of Gadd45γ−/− and Map3k4−/− embryonic gonads.