Figure 3.
Split-CRAC Allows the Targets of the N-Terminal and C-Terminal Regions of Rrp44 To Be Distinguished
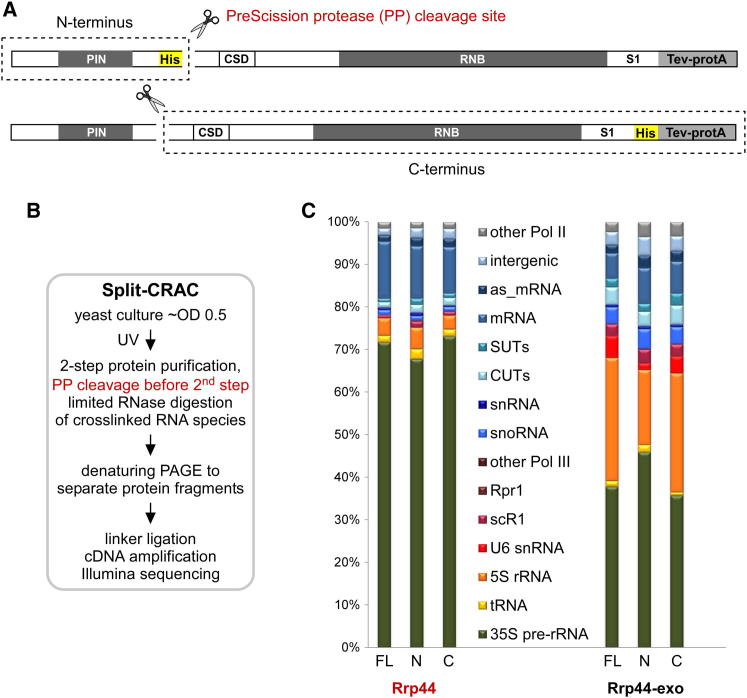
(A) Cleavable Rrp44-expression constructs used for split-CRAC. The location of the PreScission protease (PP) cleavage site, which allows the separation of N- and C-terminal domains (NTD and CTD) in vitro, and the purification tags are indicated.
(B) Outline of the split-CRAC crosslinking technique.
(C) Distribution of reads recovered with full-length and cleaved wild-type Rrp44 (left) and the Rrp44-exo mutant (right). Sequencing data were analyzed as in Figure 1.