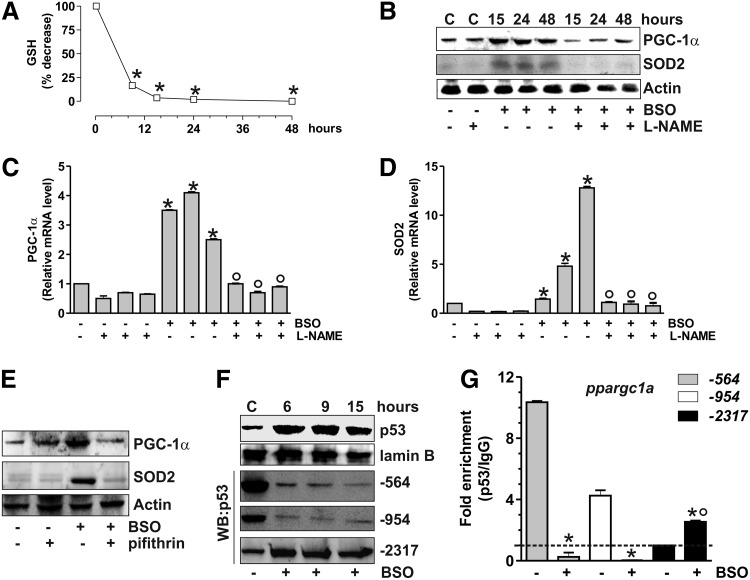
FIG. 6.
p53 modulates PGC-1α transcription in murine C2C12 cells upon GSH depletion. (A) C2C12 cells were treated with BSO (1 mM) for the indicated times. GSH content was assayed by HPLC, and data are expressed as percentage of decrease with respect to controls and reported as means±SD (n=4, *p<0.001 vs. control). (B) C2C12 cells were treated with BSO and/or L-NAME (0.1 mM) for the indicated times. Cells were lysed, and 20 μg of proteins was used for Western blot analysis of PGC-1α and SOD2. Total RNA was isolated, and relative mRNA level of PGC-1α (C) and SOD2 (D) was analyzed by RT-qPCR. Data are expressed as means±SD (n=4, *p<0.001 vs. control, °p<0.001 vs. BSO and NAME-treated cells). (E) Pifithrin (0.02 mM) was added 1 h before BSO treatment (15 h) and maintained throughout the experiment. Cells were lysed, and 20 μg of proteins was loaded for Western blot analysis of PGC-1α and SOD2. (F) After BSO treatment, C2C12 nuclear protein extracts (500 μg) were subjected to Western blot analysis of p53 and oligo-pulldown assay by using the biotinylated oligonucleotides representing the three p53REs on the ppargc1a promoter (−564, −954, and −2317). (G) After 15 h from BSO treatment, ChIP assay was carried out on cross-linked nuclei from C2C12 cells by using p53 antibody, followed by qPCR analysis of p53REs on the ppargc1a promoter (−564, −954, and −2317). Dashed line indicates the value of IgG control (n=3, *p<0.001 vs. control; °p<0.01 vs. IgG).