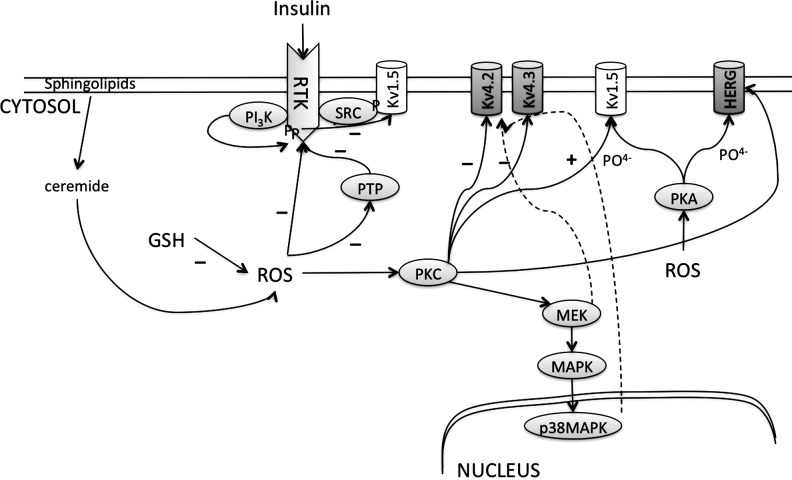
FIG. 10.
ROS effects on the voltage-gated K+channels. Phosphorylation of Kv1.5, Kv4.2, Kv4.3, or HERG decreases the currents from these channels. ROS activate PKC or PKA that are responsible for this phosphorylation. ROS also inactivate protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP), causing increased phosphorylation of the receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) that leads to activation of SRC-mediated phosphorylation of Kv1.5. ROS content is increased by cytosolic fatty acids such as ceramide and decreased by GSH.