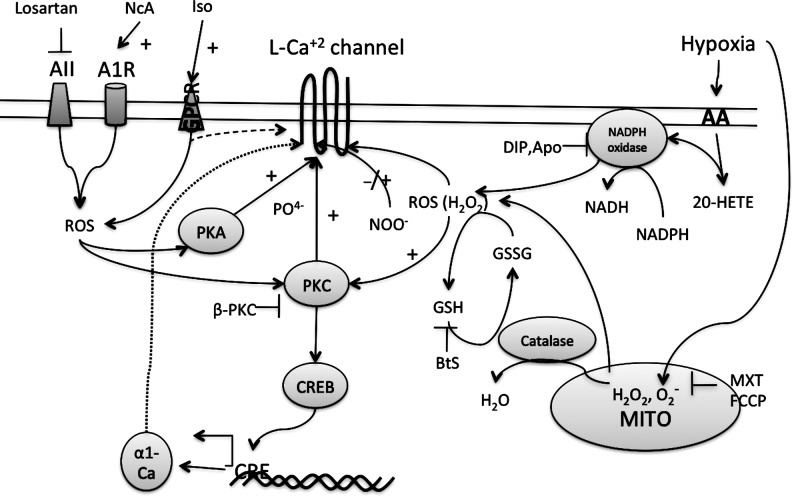
FIG. 7.
ROS induces the activity of L-type Ca+2 channels. Activation of various receptors such as angiotensin (AII) receptor, adenosine receptor (A1R), or GPCR increases ROS in the myocytes. Cytosolic ROS activate PKC or PKA that activates the channels by phosphorylation. PKC also activates CRE-binding protein (CREB) that binds to cAMP-response elements (CRE) on DNA to induce the expression of α-1 subunit of the L-type Ca+2 channels. BtS, buthionine sulfoxime; MXT, myxothiazol; FCCP, carbonylcyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone, a protonophore and uncoupler of mitochondrial respiratory chain; DIP, diphenylene iodonium; Apo, apocynin; 20-HETE, 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; AA, arachidonic acid; NcA, N-acetylcysteine; Iso, isoproterenol.