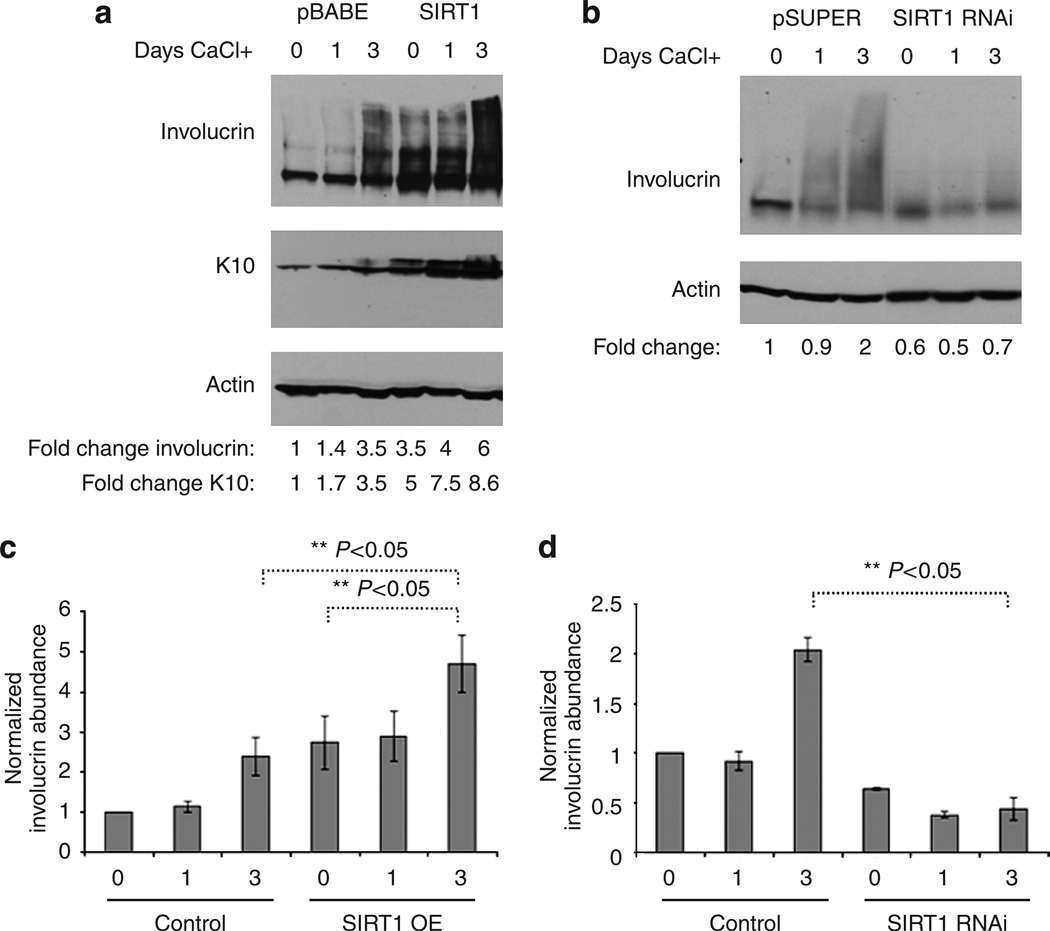
Figure 4. SIRT1 upregulation induces and SIRT1 downregulation inhibits calcium-dependant keratinocyte differentiation.
(a) NHEK cells infected with control virus (pBABE) or SIRT1 overexpression virus (SIRT1) were harvested before the CaCl2 addition (0), 1 day after the addition (1), and 3 days after addition (3). Proteins were extracted, and a western blot was run to detect involucrin, K10, and actin. A representative blot from three different experiments is shown. (b) NHEK cells infected with control virus (pSUPER) or SIRT1 RNAi virus (SIRT1 RNAi) were harvested before the CaCl addition (0), 1 day after the addition (1), and 3 days after the addition of 1.6 mm Ca2+ (3). Proteins were extracted, and a western blot was run to detect involucrin and actin. A representative blot from three different NHEK experiments is shown. (c and d) Statistical analysis of three biological replicates for SIRT1 overexpression and RNAi, respectively. Panels c and d show mean ± SEM for each treatment. SIRT1 overexpression increases normalized involucrin abundance (t-test, P<0.05). The combination of calcium and SIRT1 further increases the level of normalized involucrin abundance (t-test, P<0.05). Panel d shows that SIRT1 RNAi has the opposite effect (t-test, P<0.05).