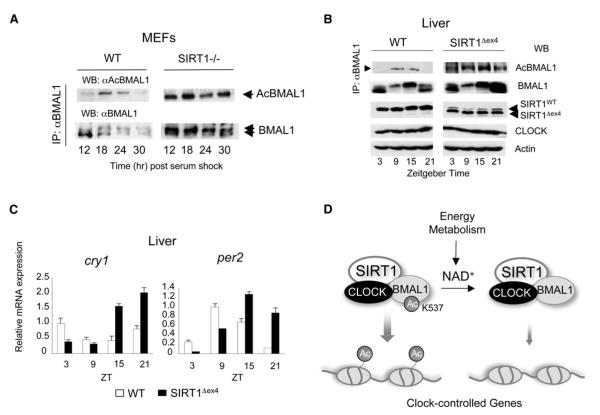
Figure 7. Circadian Dysfunction and BMAL1 Upregulated Acetylation in Liver-Specific SIRT1-Deficient Mice.
(A) BMAL1 Lys537 acetylation profile in WT or SIRT1-deficient MEFs was investigated. Cell extracts prepared from indicated time points were immunoprecipitated with BMAL1 antibody and acetylation of BMAL1 was detected by probing with the acetylated BMAL1 antibody.
(B) BMAL1 Lys537 acetylation profile in WT and SIRT1Dex4 mice was investigated. Liver extracts prepared from indicated time points were immunoprecipitated by BMAL1 antibody and acetylation of BMAL1 was detected by using the acetylated BMAL1 antibody. Acetylation of BMAL1 in the SIRT1-Dex4 mutant mice is non-rhythmic and elevated compared to WT mice. Overall levels of BMAL1 are also higher in the SIRT1-Dex4 mutant mice. The pattern of BMAL1 phosphorylation is also altered (see also Figure S5). The lower SIRT1 band corresponds to the SIRT1-Dex4 deletion. Levels of the CLOCK protein and actin were used as control.
(C) Altered circadian expression of Cry1 and Per2 clock genes in the livers of SIRT1Dex4 mice. Error bars represent SEM.
(D) Scheme of the NAD+-dependent regulation exerted by SIRT1 on the circadian clock machinery. SIRT1 interacts with CLOCK and thereby establishes a functional and molecular link between energy metabolism and circadian physiology.