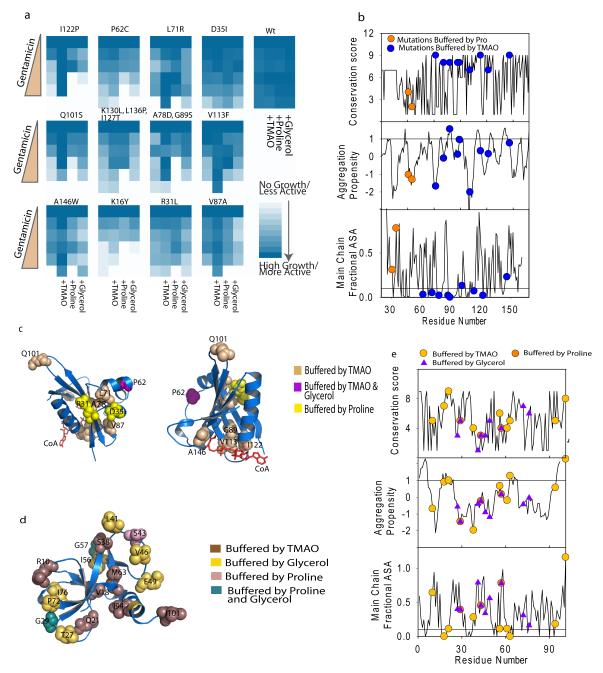
Figure4.
Chemical chaperones have specific spectrum of mutational buffering. (a). Gentamicin resistance of 12 random mutants in presence of osmolytes is shown as colormap. WtGmR transformed cells were taken as control. (b) Properties of mutated residues are plotted. Conservation (top panel), aggregation propensity (middle panel) and main chain fractional accessible surface area (bottom panel) are shown along with the residues that were buffered by the osmolytes. Line in the middle panel at aggregation propensity value of 1 denotes the generally accepted cutoff value; peptide segments above this value are considered to be aggregation prone. The line in the lower panel signifies the ASA of 0.1. Residues lying below this line are considered to be completely buried. (c) Residues buffered by osmolytes are mapped on the crystal structure of GmR, 1bo4. Color codes are listed in the legend. (d) Residues involved in mutational buffering is mapped to the crystal structure of Ccdb, 3vub47 (e) Properties of CcdB mutants were analyzed as described in (b) (see also Supplementary Figure 20-27).