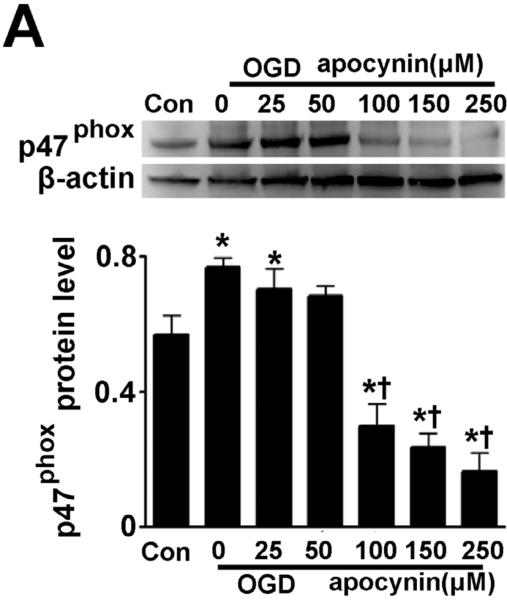
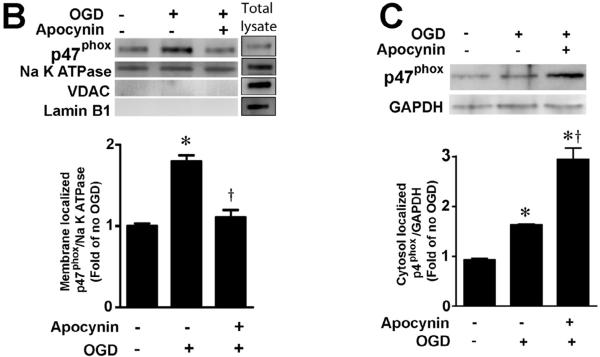
Figure 1. Oxygen glucose deprivation increases p47phox protein levels in rat hippocampal slice cultures.
Rat hippocampal slice cultures were exposed to OGD in the presence or absence of the NADPH oxidase inhibitor, apocynin (0–250μM, 2h prior to OGD). Slices were harvested 8h after OGD and subjected to Western blot analysis to determine effects on total p47phox protein levels. A representative blot is shown (A). Protein loading was normalized by reprobing with β-actin and the data plotted as the ratio of p47phox:β-actin. In addition the affect of OGD on membrane (B) and cytosolic (C) localized p47phox was determined. Again representative images are shown. Loading of the membrane fraction was normalized by reprobing with NaK ATPase and the data plotted as the ratio of p47phox: NaK ATPase normalized to 1.0 for the control. Similarly, loading of the cytosolic fraction was normalized by reprobing with GAPDH and the data plotted as the ratio of p47phox: GAPDH normalized to 1.0 for the control. Data are presented as mean ± S.E from 4 independent experiments using 24 pooled slices per experiment. * P<0.05 vs. control, † P<0.05 vs. OGD alone.