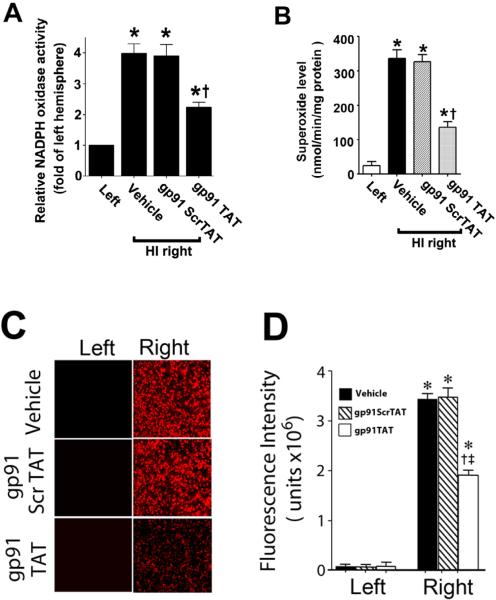
Figure 9. gp91ds-tat treatment attenuates NADPH oxidase activity and superoxide generation in the neonatal rat brain exposed to hypoxia-ischemia.
P7 neonatal rats were pre-treated with gp91ds-tat, the scrambled control peptide, or vehicle then exposed to HI. Two hours after HI, NADPH oxidase activity (A) was determined in the left and right hemispheres of the brain. Superoxide levels were also determined using both EPR (B) and DHE oxidation (C & D). There is a significant increase in both NADPH oxidase activity and superoxide levels in the right hemisphere of the neonatal brain that is attenuated by gp91ds-tat, but not the scrambled peptide. Values are presented as mean ± S.D. from 5–6 animals per group. *p<0.05 vs. left hemisphere, †p<0.05 vs. HI + vehicle.