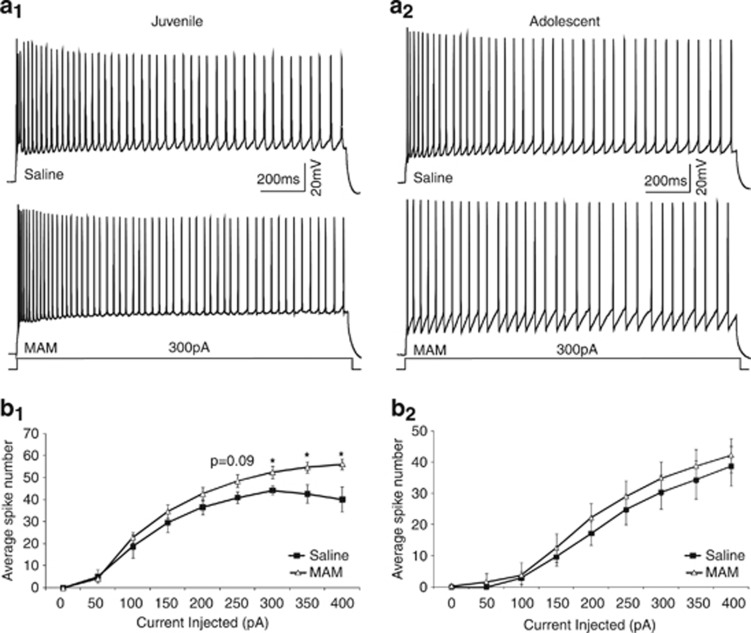
Figure 2.
MAM exposure slightly increases excitability of CA1 pyramidal neurons in hippocampus in juvenile animals. Representative action potentials (a1 and a2) and summary graphs (b1 and b2) from juvenile and adolescent saline and MAM-exposed animals. (a1 and b1) Juvenile MAM-exposed animals had an increased spike number only with high current injection compared with saline controls (saline n=6, MAM n=7, *p<0.05). (a2 and b2) There is no difference in neuronal excitability in adolescent animals (saline n=11, MAM n=12, p>0.05).