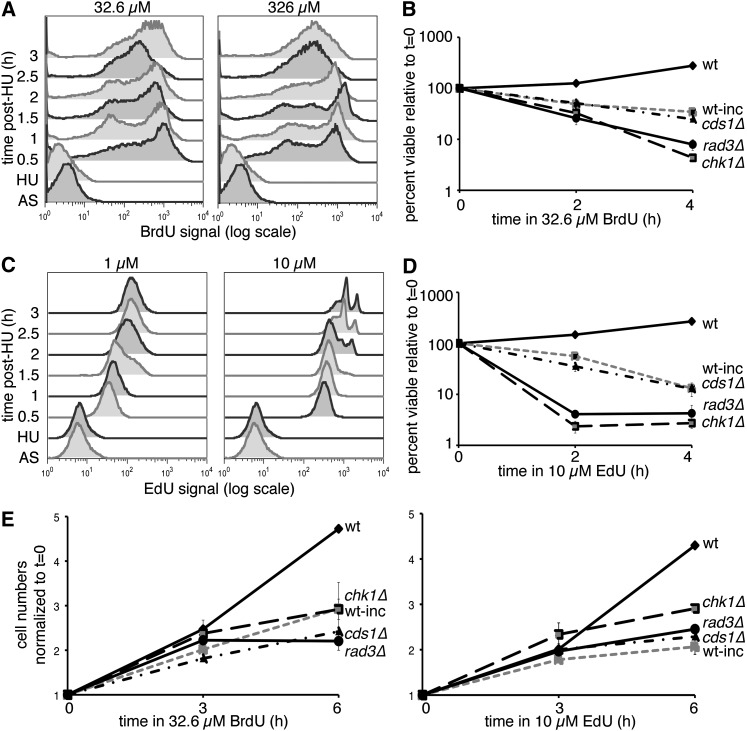
Figure 1 .
BrdU and EdU doses affect signal, viability, and cell division. (A) Time course of incorporation at 32.6 or 326 µM BrdU in HU-synchronized cells after release. Asynchronous (AS) cultures were blocked for 4 hr in HU (HU time point) before release at 32° in medium with BrdU at the indicated concentration. BrdU signal was detected in isolated nuclei. (B) Relative viability during 32.6 µM BrdU incubation, comparing nonincorporating (wt) or hsv-tk+ hENT+ cells, both wild type (wt-inc) and checkpoint mutants. Means ± SEM of three experiments are shown. (C) As in A, time course of EdU incorporation at 1 and 10 µM doses in HU-synchronized cells postrelease. Whole cells were treated with ClickIt reaction before flow cytometry. (D) Relative viability in 10 µM EdU treatment over time for nonincorporating (wt) or incorporating wild-type (wt-inc) or checkpoint-mutant incorporating cells. Means ± SEM of three experiments are shown. (E) Cells were counted during BrdU or EdU treatment to determine proliferation in nonincorporating (wt) or hsv-tk+ hENT+ wild-type (wt-inc) and checkpoint-mutant cells. Cell concentrations were normalized to the 0-hr sample for each cell line/condition and are shown as means ± SEM (n = 3).