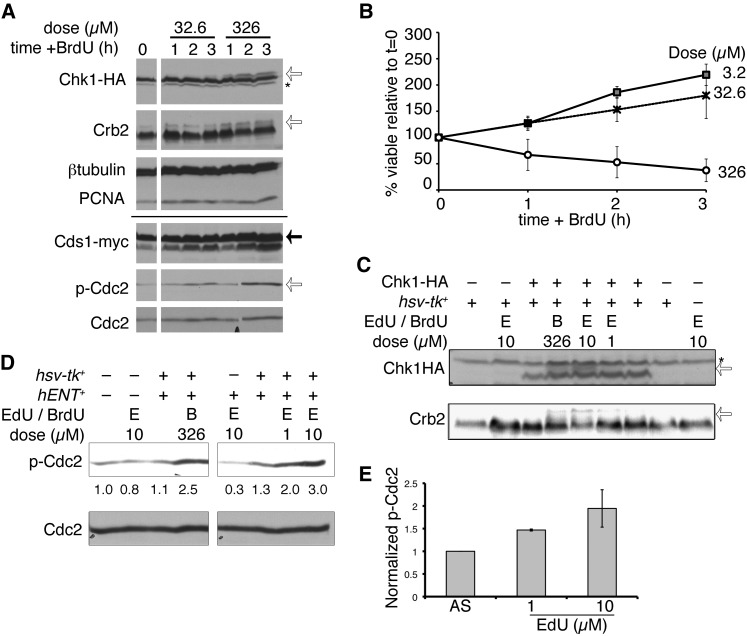
Figure 4 .
BrdU exposure triggers the DNA damage response. (A) Cells were treated with the indicated dose of BrdU and harvested for protein extraction hourly. Chk1-HA was detected with anti-HA (16B12); the asterisk indicates nonspecific background signal and the open arrow indicates phospho-Chk1HA. Crb2 modification is also indicated by an open arrow. Cds1-myc was detected with anti-myc (solid arrow). Phospho-Cdc2 (p-Cdc2, open arrow) and Cdc2 were also detected. PCNA and β-tubulin are loading controls. The solid line indicates a split between two independent gels, with identical lysates. (B) Incorporating strain viability (FY5031) proportional to BrdU dose is shown as means of three independent experiments ± SEM. (C) Chk-HA and Crb2 phosphorylation after 3 hr EdU (µM), in wild-type hsv-tk+ or nonincorporating cells. BrdU (326 µM) is included as a control. Chk1-HA and Crb2 band shifts are indicated with open arrows. The asterisk indicates nonspecific background band (above Chk1HA) detected using a different antibody from A (αHA, 12CA5). (D) Phospho-Cdc2 (p-Cdc2) after 3 hr BrdU or EdU exposure (doses µM). Below bands are the quantified band intensities of p-Cdc2, normalized to total Cdc2 (below). (E) Quantification of p-Cdc2, relative to total Cdc2 levels, from three independent experiments. Mean values are ± SEM.