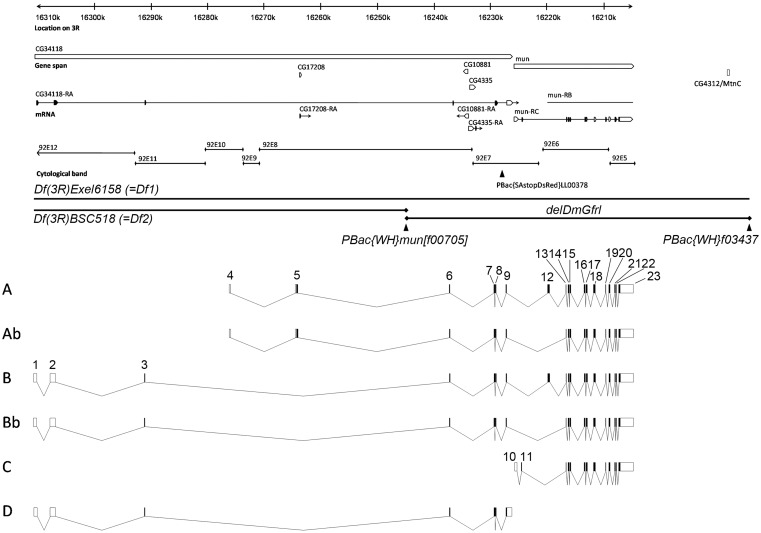
Figure 1. Genomic and transcript structure of the DmGfrl locus.
A 105-kb region of chromosome 3R is shown. The annotation is according to Flybase version FB2009_07, released August 10, 2009. On the basis of our cDNA cloning and sequencing results, the currently annotated mun/DmGfrl locus is extended into the 5′ direction by approximately 85 kb, and the genes previously annotated as CG34118 and CG17208 are fused with DmGfrl. CG4335 and CG10881, predicted intronless genes encoding a trimethyllysine dioxygenase and a translation initiation factor, respectively, are embedded on opposite strands in the 7.5-kb intron between exons 6 and 7. The Flybase entries previously annotated as CG17208 and CG34118 were identified as being the 5′ termini of the DmGfrl transcripts A and B, respectively. PBac{SAstopDsRed}LL00378 is a hypomorphic insertion utilized in the biochemical detection of endogenous DmGfrl protein (see Fig. 4). Df(3R)Exel6185 (Df1) and Df(3R)BSC519 (Df2) are the genomic deficiencies used in the genetic experiments. delDmGfrl denotes the deletion allele generated by means excision between the FRT-carrying PBac elements PBac{WH}mun[f00705] and PBac{WH}f03437. Exon-intron structures of the six DmGfrl transcripts (A, Ab, B, Bb, C, D) assembled from experimental and in silico data are presented below the genomic locus drawing. Transcripts C and D were not detected on Northern blots, which suggest that they are present at very low levels compared to the other transcripts, and thus, their physiological significance remains to be investigated.