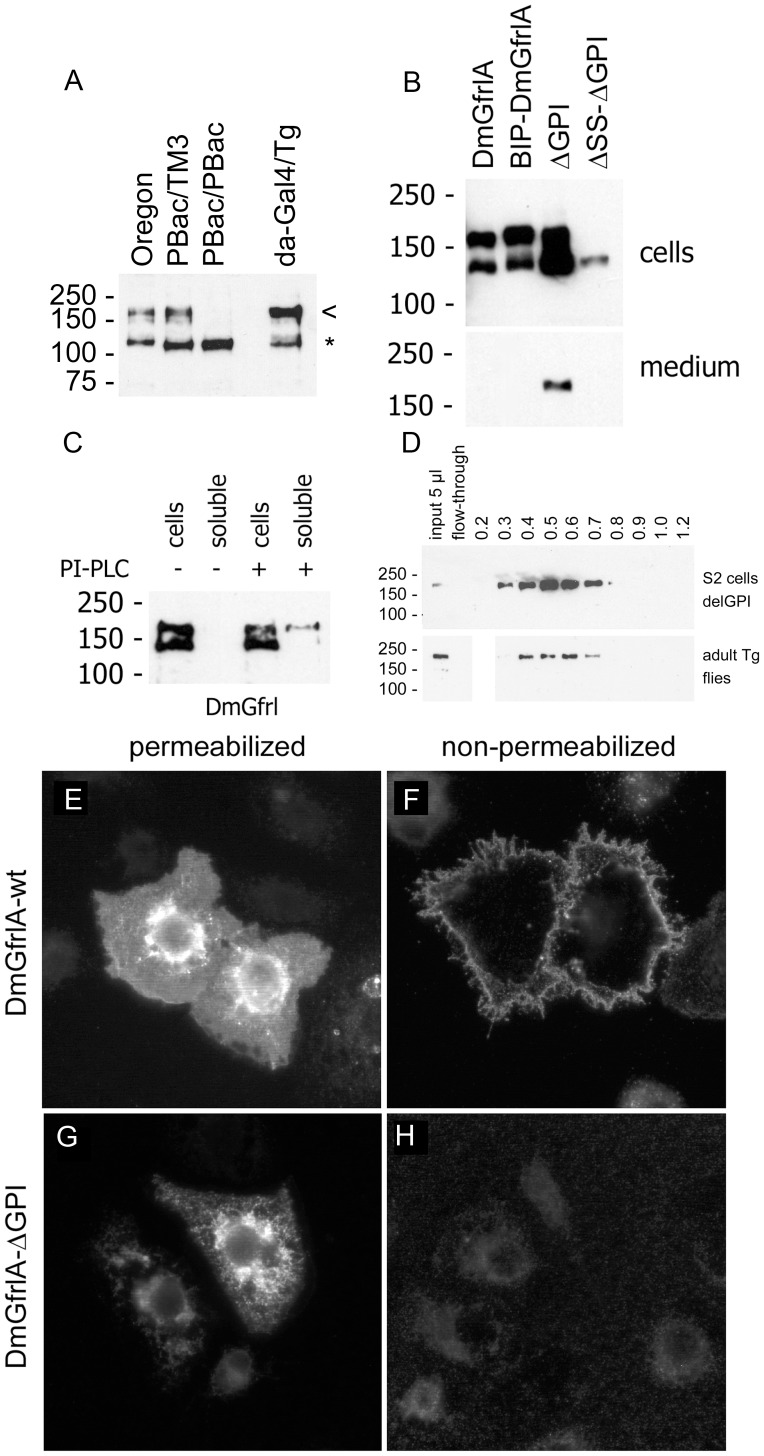
Figure 4. Detection and biochemical characterization of the DmGfrl protein.
(A) Detection of endogenous DmGfrl by immunoblotting in lectin-enriched fractions from whole adult flies. Transgenic flies expressing DmGfrlA (da-GAL4xTg) show a band of ∼170 kDa (a, arrowhead), compatible with the predicted molecular weight of the ectopic protein. In wild-type (Oregon) flies a protein species of similar molecular weight was detected. The ∼170-kDa band was also present in heterozygous (A, PBac/TM3) DmGfrl genetrap flies, but absent in homozygous (A, PBac/PBac) genetrap flies that are DmGfrl hypomorphs (our unpublished data). Asterisk denotes a non-specific band. (B) Secretion of DmGfrlA. In S2 cells transfected with N-terminally V5-tagged DmGfrlA expression plasmids bands of ∼140 and ∼170 kDa were detected (B, 1st lane). The upper and lower bands likely represent fully glycosylated cell-surface-exposed protein and partly (core N-) glycosylated immature protein being synthesized and modified in the endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi, respectively. The wild-type protein as well as a mutant in which the putative N-terminal signal sequence was replaced by a known signal sequence (BIP, B, 2nd lane) were detected exclusively in the cellular fraction, whereas a mutant protein lacking the predicted C-terminal GPI anchor was secreted into the medium (B, 3rd lane). The secretion was abolished when the N-terminal signal sequence was deleted (b, 4th lane). DmGfrl isoform B, which harbors a different signal sequence than DmGfrlA, behaved similarly in these experiments (data not shown). (C) Digestion of intact DmGfrlA-expressing S2 cells with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC). No DmGfrl is detected in the soluble extracellular fraction after incubation without PI-PLC (C, 2nd lane). Upon digestion with PI-PLC, a fraction of DmGfrlA was released into the soluble extracellular fraction (C, 4th lane). Only the ∼170 kDa DmGfrl species (upper band) was released, indicating that it is the mature form exposed on cell surface. (D) Heparin binding properties of DmGfrl. Immunoblot analysis of heparin bound fractions showed that DmGfrl elutes between 0.3 and 0.8M NaCl with a peak at 0.5M NaCl (upper panel). Thus, it showed lower affinity for heparin than mammalian GFRα1, which has multiple heparin binding sites and elutes at above 1.0M NaCl [24]. Similarly to the protein expressed in S2 cells the majority of V5-DmGfrlA from transgenic adult flies eluted between 0.4 and 0.7M NaCl (lower panels). (E–H) Immunofluorescence analysis of the plasma membrane localization of DmGfrlA. In detergent-permeabilized S2 cells, wild-type DmGfrlA is detected in the periphery of the cells as well as in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi-like structures (E). In non-permeabilized cells, intracellular staining is absent but the peripheral staining detectable, indicating that DmGfrlA is exposed on the cell suface (F). In cell expressing GPI-deleted DmGfrlA, the peripheral plasma membrane staining is absent (G, H), indicating that wild-type DmGfrlA is GPI anchored on the plasma membrane. Original magnification was 600X.