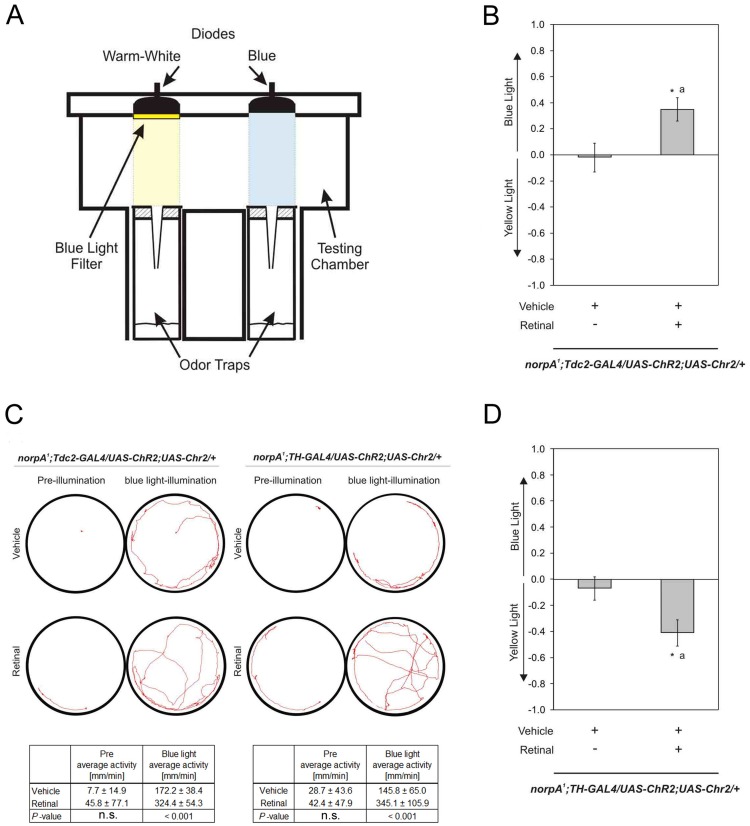
Figure 6. Neuronal activity is sufficient to induce preference. a.
The behavioral set up of the optogentic trap assay consists of two odor traps filled with food odor surrounded by a dark intransparent plastic. The assay is placed on a cold light plate to motivate flies to descend into the fly traps. On top of the two odor traps two different diodes – one for blue light and one for yellow – are placed that can be activated with the different frequencies. b Light activation of neurons in a Tdc2-GAL4 dependent manner causes preference for the trap illuminated in blue (PIs are norpA1, Tdc2-GAL4/UAS-ChR2;UAS-ChR2 with vehicle −0.02±0.11 and with retinal 0.35±0.09; n 12 for both. P<0.05.). c Typical traces of norpA1,Tdc2-GAL4/UAS-ChR2;UAS-ChR2 and norpA1,TH-GAL4/UAS-ChR2;UAS-ChR2 flies before and after a one min illumination period are shown. The average activity of 7 flies per genotype and condition are summarized in the table. d Activation of dopaminergic neurons causes aversion for the trap illuminated in blue (PIs are norpA1,TH-GAL4/UAS-ChR2;UAS-ChR2 with vehicle −0.07±0.09 and with retinal −0.41±0.1. n 20 and 35. P<0.05.).