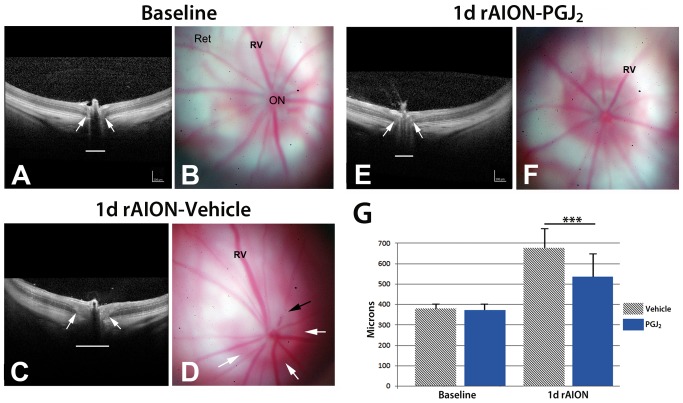
Figure 1. SD-OCT and retinal color photos of naïve, and rAION-induced vehicle and PGJ2 -treated eyes.
A,B. Naïve eye. By OCT, the retina is flat against the back of the eye. The ON shadow is narrow (arrows and white line). Retinal photo reveals the ON is flat against the retina, with no protrusion. Retinal veins (Rv) are of narrow caliber. C,D. rAION-vehicle treated. ON shows increased diameter by OCT analysis (arrows), compared with the naïve eye (compare white line lengths). The retinal photo reveals a swollen and edematous ON (delineated by the white arrows). Crossing vessels are obscured in the edematous nerve (black arrow). E,F. rAION- PGJ2 treatment. The ON shadow by OCT imaging is smaller, compared with the vehicle treated animal (Compare arrows and underlying diameter line in OCT photos of naïve, and vehicle- and PGJ2-treated, rAION induced eyes). ON edema in PGJ2-treated animals is reduced in the color photo and is similar to the naïve eye. Retinal veins (Rv) engorgement is reduced. G. SD-OCT quantification. The optic nerve diameter is equivalent in both naïve and uninduced PGJ2-treated animals. One day post-induction, the ON diameter is increased in both groups. ON diameters of PGJ2-treated animals are narrower, compared with vehicle-treated animals. The PGJ2-associated edema reduction is statistically significant (*** p<0.05; (n = 7), Bonferroni multiple comparison test).