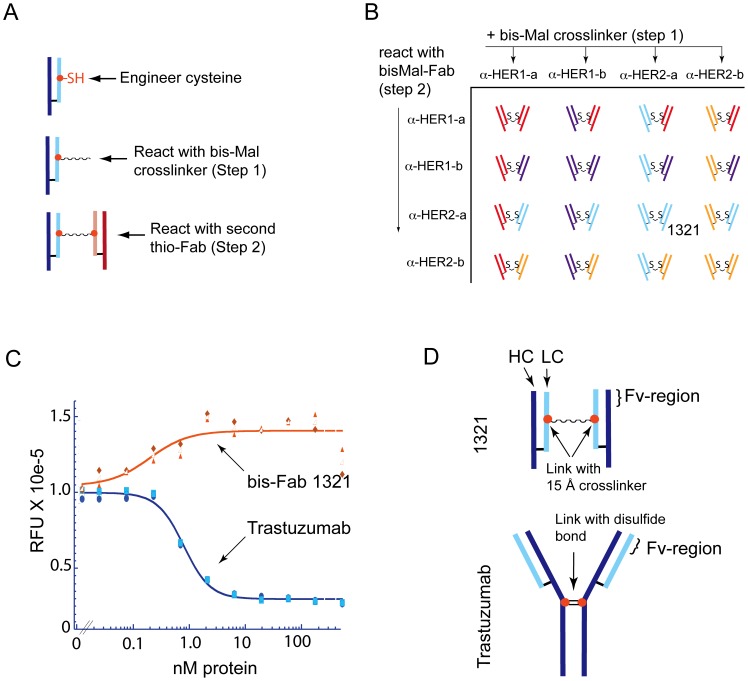
Figure 1. Agonist activity of a trastuzumab isomer.
(a) A brief description of the bis-Fab synthesis process is illustrated here. The thio-Fabs of interest are produced by engineering an unpaired cysteine into the Fab region of an antibody followed by recombinant expression and isolation of the thio-Fab containing the unpaired cysteine. A homobifunctional crosslinking reagent is then used in a two-step process to efficiently couple two thio-Fabs together. A more detailed explanation of the procedure can be found in the Experimental Methods and Figure S1. (b) A matrix combination of thioFabs using the two-step synthesis process was used to produce a panel of bis-Fab molecules for use in biological and biochemical assays. Two Fabs targeting EGFR (α-HER1-a targets domain III and α-HER1-b targets domain III) and two Fabs targeting HER2 (α-HER2-a derived from trastuzumab targets domain IV and α-HER2-b derived from pertuzumab targets domain II) were used to construct the matrix. (c) Trastuzumab and bis-Fab 1321, consisting of two trastuzumab Fabs linked together at position 110 in the light chain, were examined for their effect on cell growth. Increasing concentrations of trastuzumab (blue line) or bis-Fab 1321 (orange line) were added to BT474 cells and cell proliferation was measured after five days using AlamarBlue staining. The relative fluorescence units are reported for the different treatment concentrations. Individual data points for two independent experiments are shown in the plot as well as an average of the two, which are represented by the lines and open shapes. Trastuzumab analog (bis-Fab 1321) showed agonistic activity as measured by increased cell proliferation, whereas trastuzumab inhibited cell proliferation. (d) The schematic illustrates the site of covalent attachment between the Fabs of the parent antibody trastuzumab and bis-Fab 1321. Although the global conformations of the Fab domains are unknown, this figure highlights the distinct difference in the points of connection. The native interchain disulfides (hinge region, near HC-228) in the heavy chains of trastuzumab provided the covalent attachment site for the Fab arms in the antibody. In contrast, bis-Fab 1321 was covalently linked through light chains at LC-110 using a bis-maleimido crosslinker. The resultant molecules presented Fab Fv-regions in different relative orientations.