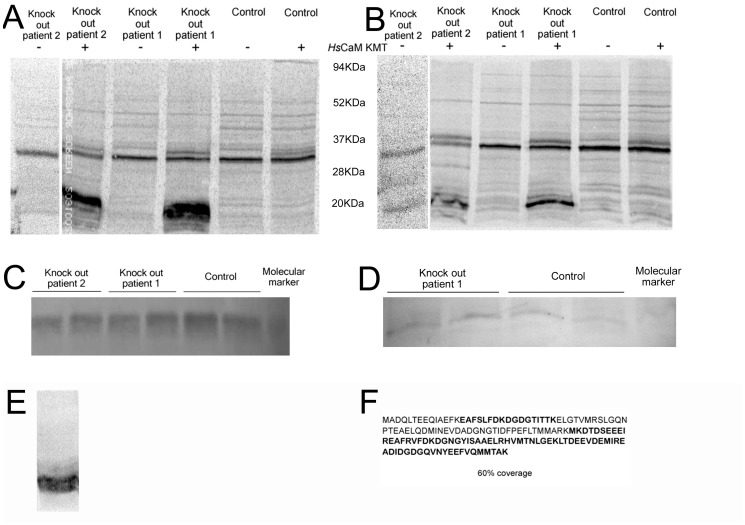
Figure 2. Analyses of the methylation status and relative amounts of CaM in lymphoblastoid cell lysates from a patient affected by the 2p21 deletion syndrome.
(A) Phosphorimage of cell lysates from two 2p21 deletion syndrome patients and wild type individuals incubated in the presence of [3H-methyl] AdoMet with and without the addition of HsCaM KMT. (B) Phosphorimage as in panel (A) but after reduction in the level of CaM by treatment of the cell lysates with phenyl sepharose. Molecular mass markers in kDa are indicated between A and B. (C) Western blot performed with anti-CaM antibody to verify the presence of similar amounts of CaM in the 2p21 deletion syndrome patient and wild type individuals. (D) Western blot performed as in panel (C) on cell lysates after partial removal of CaM with phenyl sepharose. (E) Phosphorimage showing methylation of phenyl sepharose-bound CaM removed from 2p21 deletion syndrome patients cell lysates by the addition of HsCaM KMT and [3H-methyl] AdoMet. Molecular mass markers in kDa are indicated on the right. (F) Identification of the protein radiolabeled by incubation with [3H-methyl] AdoMet and HsCaM KMT in panel (A) as CaM by MS/MS analysis. Peptides identified after tryptic digestion are shown in bold, approximately 60% of the entire CaM sequence was identified. The arrow indicates the position of HsCaM KMT.