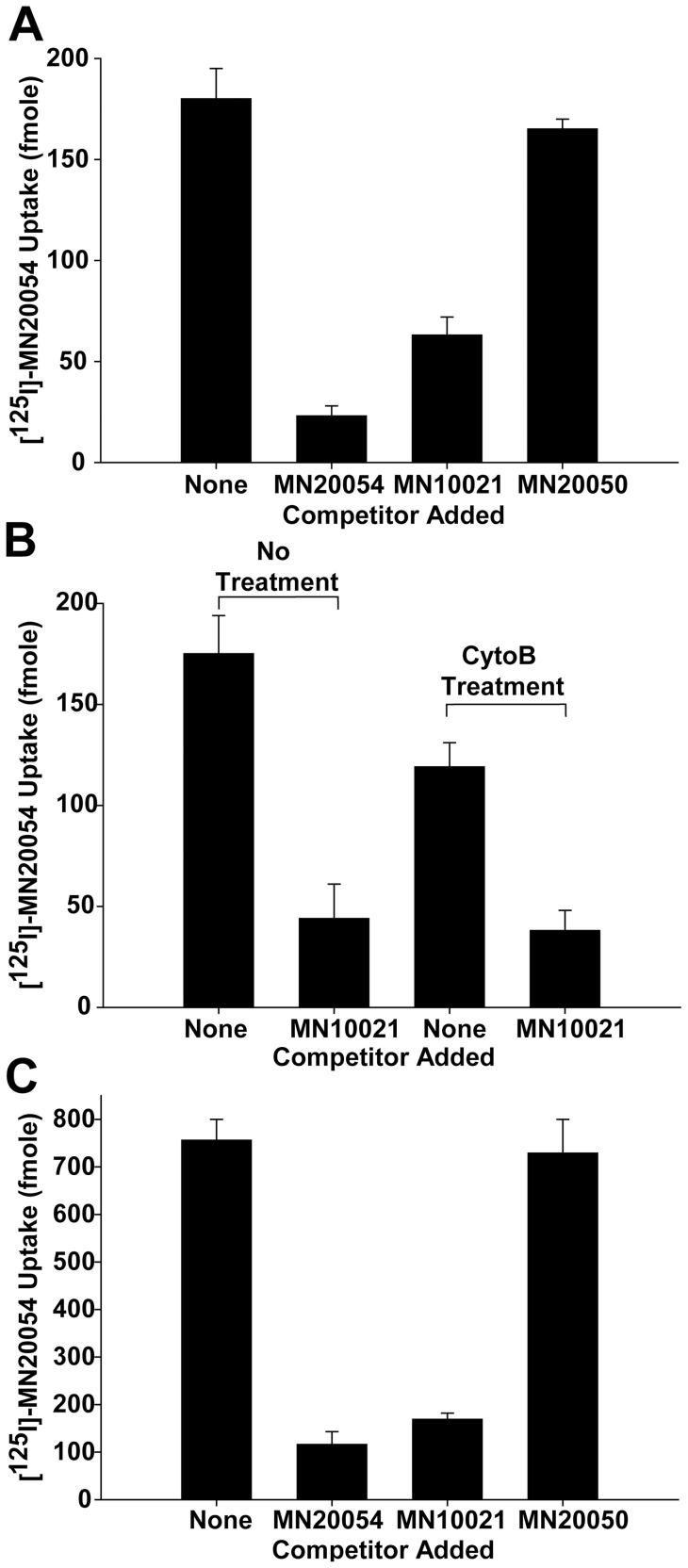
Figure 6. Monocyte and endothelial cell binding of MN10021 and MN20054.
A. Human blood monocytes, isolated as described in Methods, were adjusted to 5×106/ml in PBS (0.5% BSA, pH 7.5). Two-tenths ml of cell suspension was added to each of triplicate 12×75 mm polypropylene tubes and the tubes were incubated for 60 min at 37°C with 20 pmol of [125I]-MN20054 in the presence of either buffer alone, a 100-fold molar excess of MN20054, a 100-fold molar excess of MN10021, or a 100-fold molar excess of MN20050. The contents of each tube were then layered onto 0.8 ml of 10% sucrose in Eppendorf tubes, centrifuged, and the cell-associated radioactivity determined by gamma scintillation spectrophotometry of the cell pellet. B. Binding/uptake of [125I]-MN20054 by human monocytes was performed as described for panel A with the following exceptions: (1) half the cells were pretreated for 30 min at 37°C with cytochalasin B to inhibit endocytosis and (2) competition was performed only with a 100-fold molar excess of MN10021. C. HUVEC were grown to confluence in 12-well tissue culture plates. To each of triplicate wells was added 20 pmol of [125I]-MN20054 in the presence of either buffer alone, a 100-fold molar excess of MN20054, a 100-fold molar excess of MN10021, or a 100-fold molar excess of MN20050. The plates were incubated for 60 min at 37°C with gentle rocking, the wells aspirated and quickly washed 3X with 2.0 ml each of ice-cold PBS/BSA and 1.0 ml of 1.0 N NaOH added to each well to solubilize the cells. Nine-tenths ml of solubilized cells was then removed from each well and cell-associated radioactivity determined by gamma scintillation spectrophotometry.