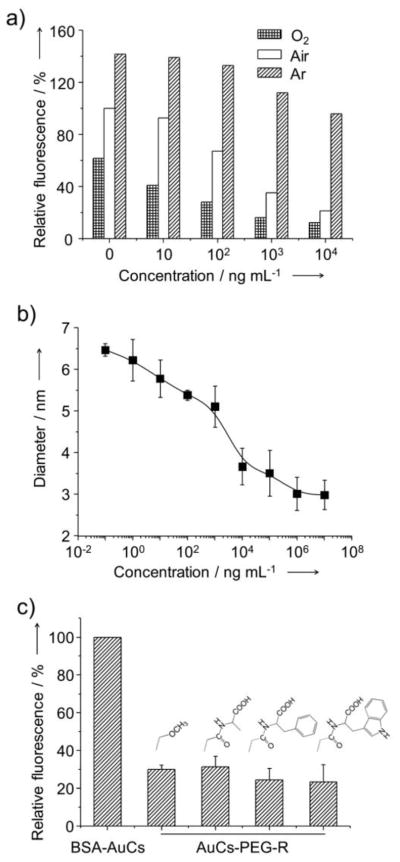
Figure 3.
(a) Dependence of the intensity of fluorescence from BSA-AuCs on the concentration of proteinase K. The aqueous suspensions of BSA-AuCs were saturated with oxygen (O2), air or argon before and during fluorescence measurements. (b) Dependence of the size of BSA-AuCs on the concentration of proteinase K. (c) Comparison of the intensity of fluorescence for aqueous suspensions of AuCs conjugated with amino acids or methoxy group using PEG as the linker. The amino acids (alanine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine) were first conjugated with succinimidyl propionyl PEG disulfide (Mw ≈ 2,000) and then reacted with BSA-AuCs. The fluorescence intensities were in reference to that of BSA-AuCs incubated in ambient air without proteinase K.