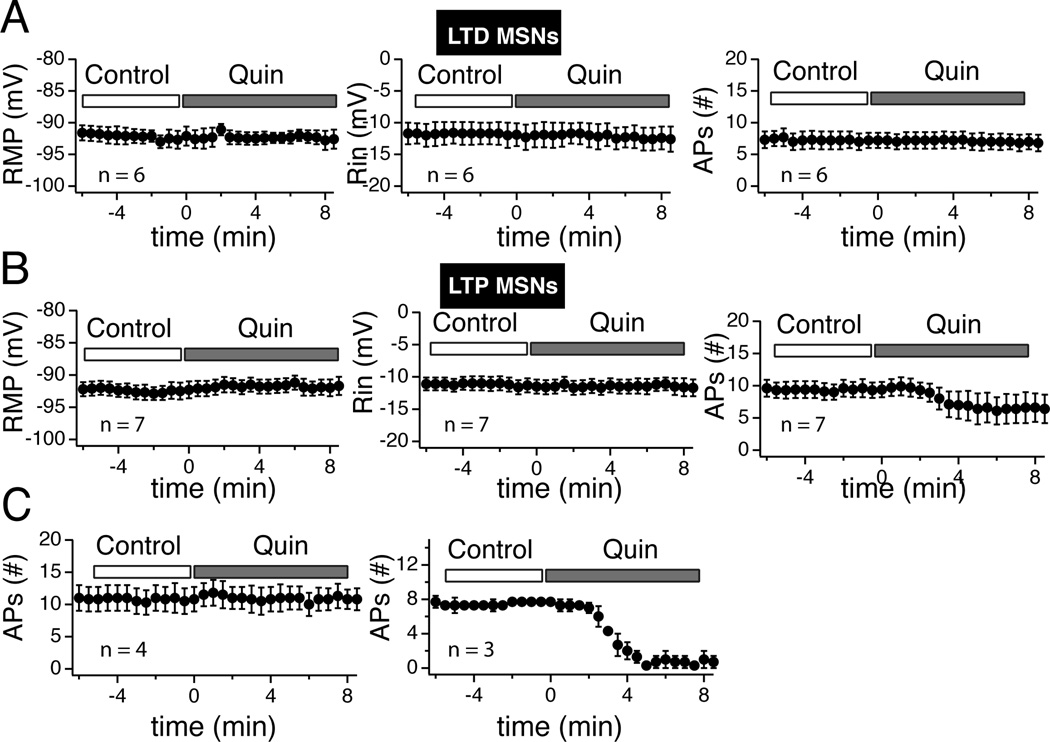
Figure 12. Quinpirole failed to alter tLTD- but inhibited tLTP-MSNs.
A Averaged values of RMP (left panel), Rin (middle panel), and number of action potentials (right panel) monitored every 30 sec before (control) and during quinpirole (Quin) exposure in tLTD-MSNs (n = 6). Note the stability of all parameters. B Graphs show the same parameters (RMP, Rin, #APs) in tLTP-MSNs (n = 7). Contrary to tLTD neurons, there is a noticeable decrease of the number of APs (right panel). C tLTP-MSNs shown in previous panel have been split based on their response to quinpirole. Left graph groups tLTP-MSNs showing no sensitivity to the drug. Right panel shows the number of action potentials from the subset of tLTP neurons (n = 3) whose firing patterns were inhibited by quinpirole.