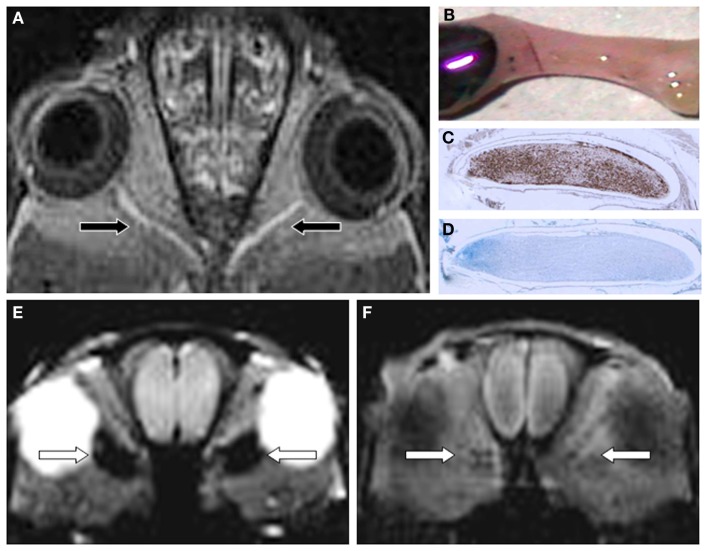
Figure 2.
Gf improves EAE lesion detection in optic nerves (ON) belonging to the CNS (A-D). Twenty-four hours after systemic administration of Gf coronal T1-w MRI shows bilateral disturbance of the blood-optic nerve barrier [arrows in (A)]. The macroscopic preparation of the left ON (B) confirms extravasation of labeled Gf. Thereafter the ON was embedded in paraffin and longitudinal sections were stained for macrophages (ED-1) (C) and myelin (Luxol fast blue) (D). Note that the Gf enhancing ON is heavily infiltrated by ED-1 positive macrophages (C) and almost completely demyelinated [lack of deep blue staining in (D)]. (E,F) depict the spatial discrepancy between cellular inflammation and BBB dysfunction in EAE. Coronal CISS (constructive interference steady state) MRI of a severely affected rat 24 h after SPIO application shows strong signal loss in both optic nerves [arrows in (E)]. By contrast, the same animal lacks retrobulbar Gf enhancement on corresponding T1-w MRI 24 h after Gf administration (F) indicating that macrophages infiltrated the ON without concomitant disturbance of the blood-optic nerve barrier. Since acute macrophage infiltration as shown in (E) does not immediately cause leakage of the BBB allowing access of Gf (F) we speculate that BBB dysfunction is a secondary and delayed event dependent on previous macrophage infiltration. Adapted from Bendszus et al. (2008) (A) and Ladewig et al. (2009) (E,F).