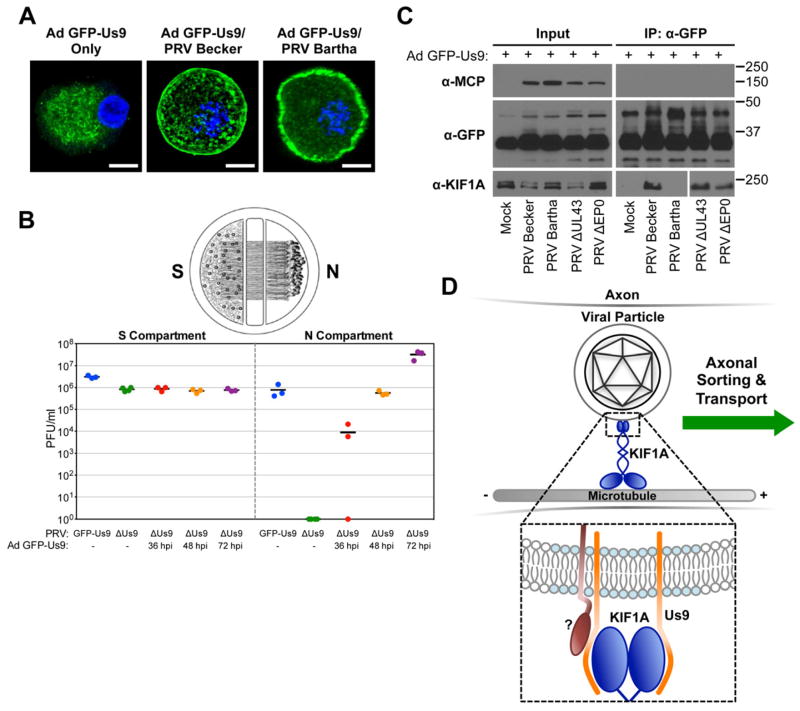
Figure 4. Us9 is necessary but not sufficient for interacting with KIF1A during PRV infection.
(A) SCG neurons were transduced with an adenoviral vector expressing GFP-Us9 (Ad GFP-Us9). At 5 days post transduction, neurons were infected with PRV Becker, PRV Bartha, or mock infected (scale bars = 10 μm). (B) Neurons grown in a trichamber were transduced with Ad GFP-Us9 in the S compartment. Us9 null PRV (PRV 161) was added at the indicated times post transduction. For comparison, we also tested PRV Us9 null and PRV expressing GFP-Us9 (PRV 340) without adenoviral transduction. The S and N compartments of all chambers were harvested at 24 hours post PRV infection and titered using a standard plaque assay. The total times of Ad GFP-Us9 transduction, including the PRV infection period, are the indicated times plus 24 hours. (C) PC12 cells were transduced with Ad GFP-Us9 for 4 days and then infected with the indicated PRV strains or mock infected. Cells were lysed at 12 hours post PRV infection and subject to immunoaffinity purification using anti-GFP antibodies as previously described. (D) Schematic model of Us9-dependent axonal sorting and transport of viral particles. Our data indicate that the membrane protein Us9 (orange) recruits KIF1A (dark blue) to intracellular viral particles contained within transport vesicles. Us9 must be incorporated within membrane microdomains known as lipid rafts (light blue) to interact with KIF1A. At least one additional viral protein (dark red) is required to facilitate the interaction between Us9 and KIF1A.