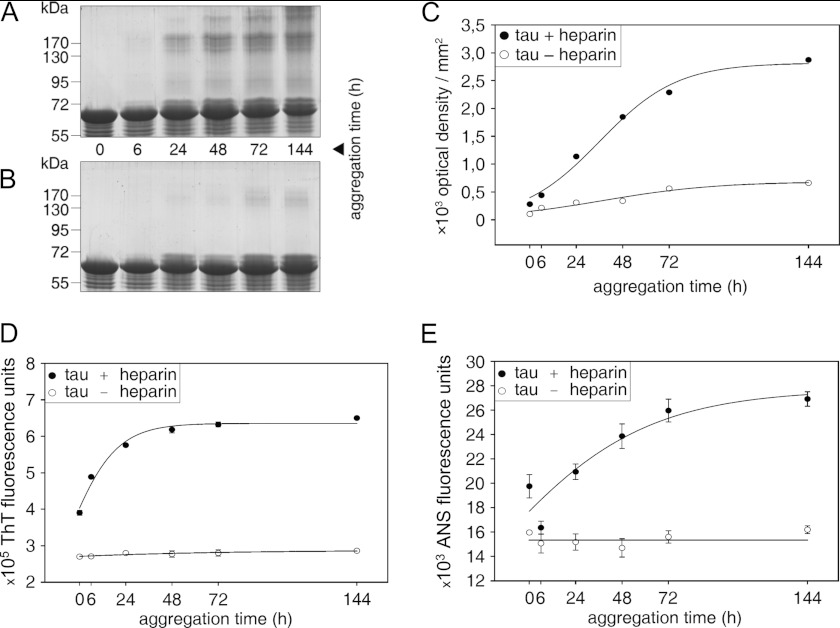
FIGURE 1.
Monitoring Tau aggregation. Tau was aggregated for different periods of time (0, 6, 24, 48, 72, and 144 h) with (A) and without (B) heparin. Tau aggregation was visualized by separating aggregation samples by 10% SDS-PAGE, followed by protein staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250. A, increasing aggregation time leads to an increase of high molecular weight Tau aggregates above the Tau monomer band at 63 kDa. B, incubation of Tau without heparin does not lead to formation of high molecular weight products. Please note shifted Tau bands in the range of 65–72 kDa in A and B, which probably represent conformationally changed monomeric Tau. C, densitometric analysis also reveals an increase of high molecular weight Tau aggregates with increasing incubation time if Tau fibrillogenesis is induced by heparin. Tau aggregation with and without heparin was also measured by ThT (D) and bis-ANS fluorescence spectrometry (E). Both fluorescence dyes indicate Tau protein aggregation in the presence of heparin, whereas Tau protein aggregation does not occur in the absence of heparin. Data are expressed as mean values ± S.D. (error bars).