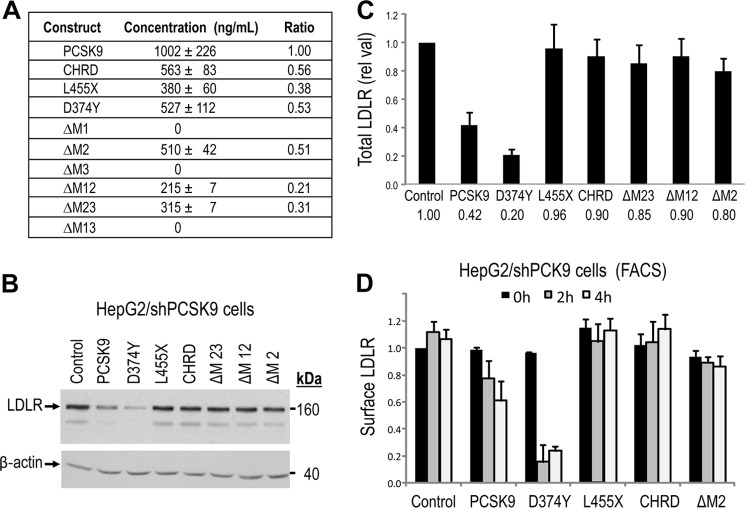
FIGURE 3.
Lack of modulation of LDLR levels following extracellular incubation of HepG2/shPCSK9 cells with CHRD module deletants. A, ELISA-V5 assay of secreted PCSK9, L455X, CHRD, D374Y, and CHRD deletants (ΔM2, ΔM12, and ΔM23) from transiently transfected HEK293 cells. B and C, HepG2/shPCSK9 cells were incubated with equal amounts of PCSK9 constructs (1.2 μg/ml) for 4 h at 37 °C. Cells were then lysed, and total LDLR levels were analyzed by Western blot analysis (B) and normalized to β-actin (C). Total LDLR was detected using a polyclonal antibody recognizing its extracellular domain, and all PCSK9 constructs were detected with a V5 HRP-conjugated antibody. D, HepG2/shPCSK9 cells were incubated for 0, 2, and 4 h at 37 °C with equal amounts (1.2 μg/ml) of secreted PCSK9 constructs, including ΔM2. Cells were detached as described under “Experimental Procedures,” and the levels of cell surface LDLR were measured by FACS analysis. As negative controls we used either a construct lacking the CHRD (L455X) or that expressing only the CHRD, both of which had no effect on LDLR levels, similar to the PCSK9 ΔM2 construct. These data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Only PCSK9 and its D374Y mutant significantly (p < 0.001) enhance the degradation of the LDLR.