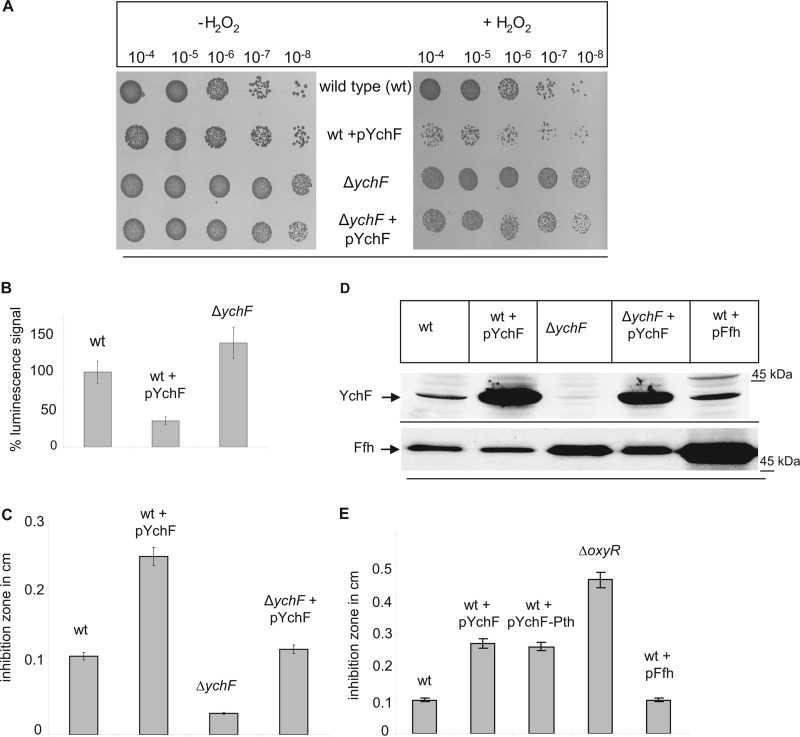
FIGURE 1.
Overexpression of YchF in E. coli leads to H2O2 hypersensitivity. A, the indicated strains were inoculated in LB medium and grown to an A600 of ∼0.5 before stepwise dilution in LB medium. From each dilution, 10-μl cell suspensions were spotted onto LB plates in the presence or absence of 2 mm H2O2. Cell growth was analyzed after overnight incubation at 37 °C. B, cells were adjusted to an A600 of 0.5 and after a 1:10 dilution treated with 10 mm H2O2 in PBS for 50 min at 25 °C. After a wash step, 100 μl of the cell culture was transferred to a 96-well plate, 100 μl of the BacTiter-Glo microbial cell viability assay solution was added, and luminescence was recorded. The luminescence signal of wild type E. coli was set to 100%. Shown are the mean values of at least three independent experiments. The error bars indicate the standard deviation. C, for the agar diffusion assay, E. coli cells were mixed with top agar and poured onto LB agar plates. Sterile discs of filter paper were soaked with 2 mm H2O2 and placed on top of the cell agar mixture. After 4 h of incubation, inhibition zones were measured. The data were obtained in at least three independent experiments, and the mean values are shown. D, Western blot using whole cells (approximately 0.5 × 108 cells) precipitated on ice for 30 min with trichloroacetic acid (TCA). After centrifugation, the pellet was resuspended in SDS loading buffer and separated by SDS-PAGE. After Western transfer, the membrane was probed with α-YchF antibodies. As a control, antibodies against Ffh were used. E, the agar diffusion assay using the indicated strains was performed as described in C.