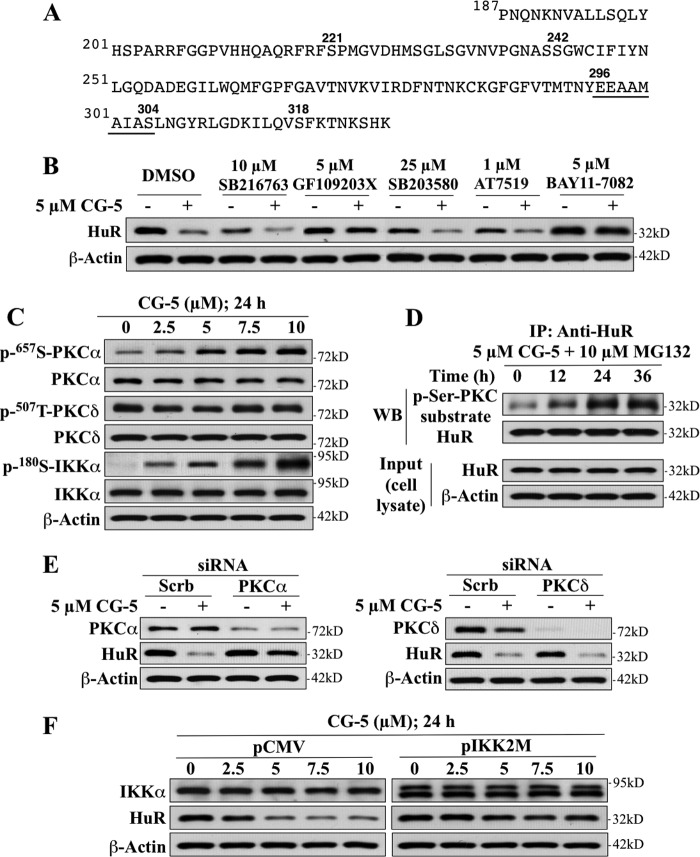
FIGURE 8.
Evidence that PKCα and IKKα play pivotal roles in CG-5-facilitated HuR degradation in LNCaP cells. A, the amino acid sequence of the HNS-RRM3 motif of HuR. B, effects of various kinase inhibitors, including SB216763 (GSK3β), GF109203X (PKC), SB203580 (p38), AT7519 (CDK), and BAY11–7082 (IKKα) on CG-5-mediated HuR degradation. Cells were treated with CG-5 in combination with individual kinase inhibitors at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. C, dose-dependent effect of CG-5 on the phosphorylation status of PKCα, PKCδ, and IKKα in LNCaP cells. D, coimmunoprecipitation analysis of the time-dependent effect of 5 μm CG-5 on PKC-mediated serine phosphorylation of HuR. Cells were treated with 5 μm CG-5 for 12 or 24 h followed by cotreatment with 10 μm MG132 for an additional 12 h. Equal amounts of cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-HuR antibody and protein A/G-agarose followed by immunoblotting (WB) with anti-p-Ser PKC substrate and anti-HuR antibodies. E, effects of siRNA-mediated silencing of PKCα versus PKCδ on CG-5-mediated HuR degradation. Cells were transfected with 100 nm scrambled (Scrb), PKCα (left panel), or PKCδ (right panel) siRNA for 48 h and were then treated with 5 μm CG-5 for 24 h. F, dominant-negative inhibition of IKKα by IKK2M protected HuR from CG-5-mediated degradation.