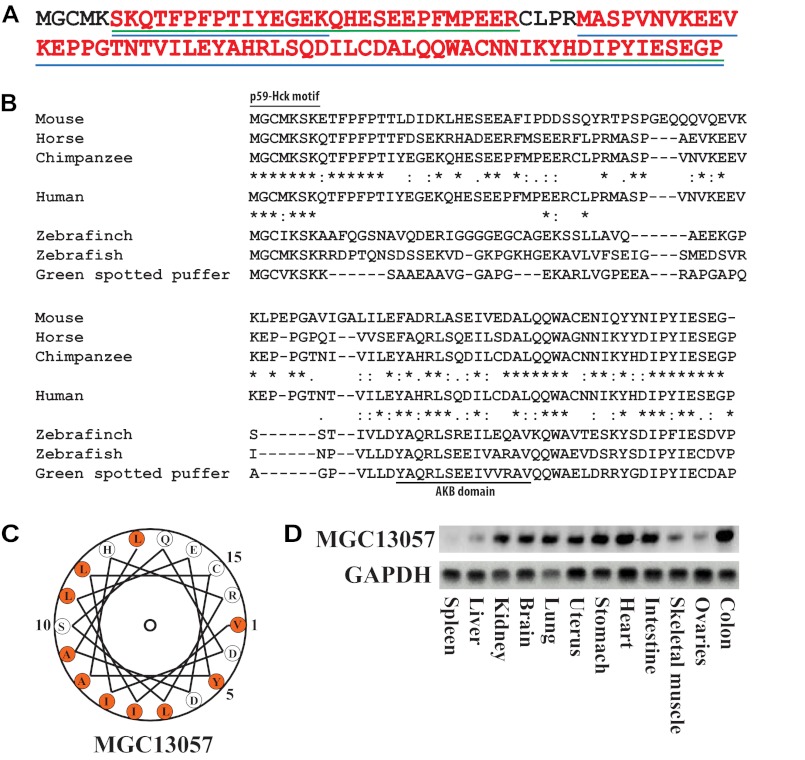
FIGURE 1.
Discovery of MGC13057 as a putative AKAP. A, a chemical proteomics analysis by means of cAMP-bound resin performed upon human heart (left ventricle) and platelets leading to the detection of the hypothetical protein MGC13057. Sequence coverage (red text) of this small protein was nearly complete with peptides identified in heart (blue lines) and platelets (green lines). B, sequence alignment of human MGC13057 with various orthologues in other species (from top to bottom: mouse (Q9CPS8), horse (XP_001502030.1), chimpanzee (XP_003309413.1), human (Q9BSF0), zebrafinch (XM_002191648.1), zebrafish (P0C8S0), and green spotted puffer (Q4RTJ5)). Identity (*) and similarity (:) in several regions, including the AKB domain and p59Hck motif are annotated. C, helical wheel alignment of the putative AKB domain revealing an amphipathic helix with a hydrophobic surface on one side (orange). D, mRNA expression of the MGC13057 gene in several mouse tissues by RT-PCR.