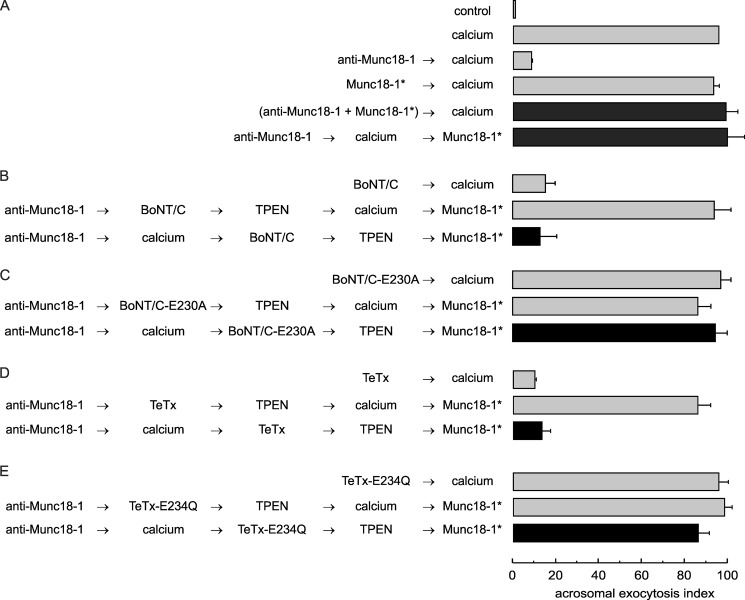
FIGURE 4.
Functional assay confirms that the anti-Munc18-1 antibody inhibits acrosomal exocytosis by preventing trans-SNARE complex assembly. A, SLO-permeabilized sperm were treated for 15 min at 37 °C with 10 nm anti-Munc18-1 antibody alone or preincubated with 40 nm of the peptide used to generate the antibody (Munc18-1*). Acrosomal exocytosis was initiated with 0.5 mm CaCl2 (37 °C for 15 min). When indicated, Munc18-1* was added at the end of the incubation to rescue the exocytotic block (37 °C for 10 min). B–E, permeabilized sperm were incubated with 10 nm anti-Munc18-1 antibody for 10 min at 37 °C followed by 0.5 mm CaCl2 to initiate exocytosis. After 10 min, 100 nm of the light chain of wild type BoNT/C (B), catalytically dead BoNT/C-E230A (C), wild type TeTx (D), or catalytically dead TeTx-E234Q (E) was added and incubated for a further 10 min to assess toxin sensitivity at the step blocked by the antibody. We stopped toxin activity with 2.5 μm TPEN for 10 min and released the block with 40 nm Munc18-1* for 10 min at 37 °C (black bars). Controls (gray bars) included the following: background exocytosis in the absence of any stimulation (control), exocytosis stimulated by 0.5 mm CaCl2, and the effect of 10 nm anti-Munc18-1 or 40 nm Munc18-1* on calcium-stimulated exocytosis. Controls also included the inhibitory effect of 100 nm wild type BoNT/C and wild type TeTx, and the lack of effect of the inactive neurotoxins. Finally, another set of controls showed that the toxins cannot affect exocytosis if cells are not stimulated and that TPEN efficiently inactivates neurotoxins. Sperm were fixed, and acrosomal exocytosis was evaluated using PSA-FITC, and data were normalized as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The values represent mean ± S.E. of at least three independent experiments. The anti-Munc18-1 antibody used for these experiments was from Synaptic Systems.