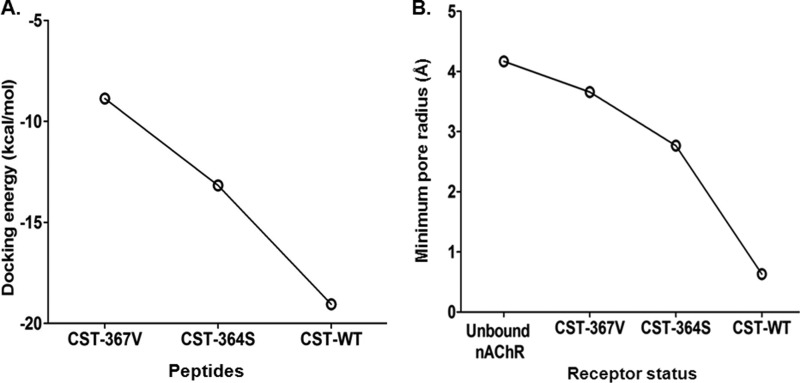
FIGURE 9.
CST variants have differential receptor binding affinity as well as receptor blockade. A, shown is a docking energy pattern of the CST variants with the human α3β4 nAChR. The docking energies for the peptides were in the following order: CST-WT (−19.05 kcal/mol) < CST-Ser-364 (−13.17 kcal/mol) < CST-Val-367 (−8.87 kcal/mol), suggesting that among these peptides interaction of CST-WT with the receptor is strongest that is followed by CST-Ser-364 and CST-Val-367, respectively. B, shown is a pore radius profile of the unbound and bound CST nAChR structures at the extracellular vestibule. CST-WT peptide showed minimum pore radius thereby creating minimum solvent accessible pathway through the pentameric ion channel corroborating with its highest potency for inhibition of channel function. The order of the minimum pore radius for the CST peptides bound to nAChR was as follows: free nAChR > CST-Val-367 > CST-Ser-364 > CST-WT.